What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)? Meaning & Examples Explained
What is the Internet of Things? This guide defines the Internet of Things (IoT) while providing examples of how it is used, why it’s important, and its benefits and challenges. While the IoT makes real-time processes possible, its data needs can get intensive.
The Internet of Things (IoT) used to be a futuristic concept, but we are now living in that future, where many of our devices (both domestic and non-domestic) are connected or can be connected. What is the Internet of Things, though?
At its simplest, the IoT facilitates data collection from all kinds of devices and leverages robust cloud computing resources for data-intensive processes. Read on as we unravel what the Internet of Things means and go over some examples, plus why it’s important.
-
03/14/2025 Facts checked
We rewrote this article to give a more up-to-date explanation of the IoT in an easier-to-read format.
Definition: What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a framework of interconnected devices (physical objects) that collect data from their environment and exchange collected data with other devices within their network. In some cases, the devices may even process data.
Traditionally, actual computers collect and process data. However, with the IoT, the scope of data collection, transfer and processing extends to many other physical objects, including thermostats, refrigerators, watches, vehicles, cameras and RFID tags, with the goal of ensuring real-time data handling.
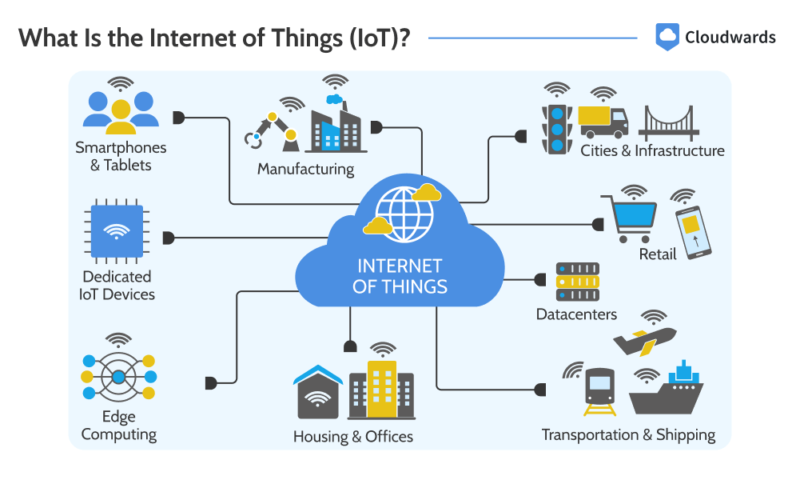
How Is IoT Used?
The IoT is used in various parts of daily life, both domestically and non-domestically. For example, in homes, the IoT is used in smart home devices for automating security systems and regulating utilities, among other things.
In the healthcare industry, IoT’s uses include remote patient monitoring and medical alerts; in manufacturing, use cases include inventory tracking and quality control. The IoT is also used for transportation, public infrastructure, agriculture and more.
Why Is IoT Important?
The IoT is important because it enhances productivity, increases safety, promotes resource management and accelerates innovation.
What Technologies Made IoT Possible?
The technologies that made the IoT possible include cloud computing, edge computing, IPv6, wireless connectivity and sensors. Each one contributes to an IoT platform in the following ways:
- Edge computing: Edge computing allows for real-time data processing by bringing the required resources closer to IoT devices. It is ideal for IoT applications that require rapid decision-making to function.
- Cloud computing: Cloud computing provides the resources to store and process large volumes of data, especially when edge computing resources are not able to efficiently handle such large data volumes.
- IPv6: IPv4 (the first version of the Internet Protocol) offers only 4.3 billion IP addresses, which is insufficient for all the devices on the internet. However, IPv6 offers more than 340 undecillion IP addresses, which is more than enough for the foreseeable future — particularly for IoT devices, which are multiplying exponentially.
- Wireless connectivity: IoT devices communicate with each other using various wireless technologies, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
- Sensors and actuators: Sensors and actuators are crucial parts of IoT devices. The devices use sensors to gather data from their environment, and they use actuators to perform actions in response to the data they collect.
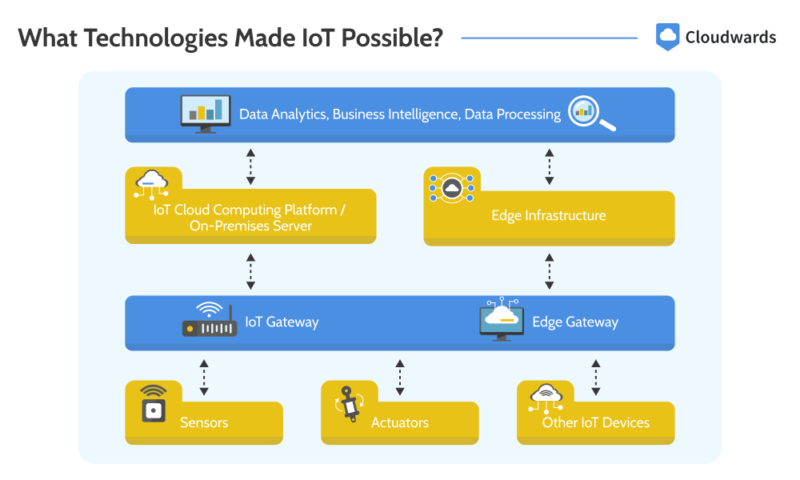
that most end users interact with.
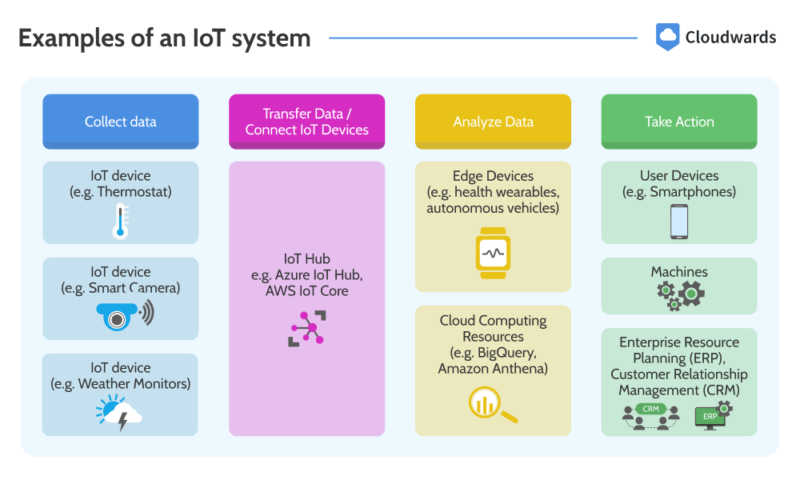
IoT Examples
The IoT is used across various industries of the global economy, including healthcare, manufacturing, retail, agriculture and homes. Let’s look into some examples of the IoT across these industries:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, the IoT is commonly used for patient monitoring through wearable devices and implants. In addition, some devices are used for controlled drug administration (e.g., connected inhalers), while others help with physical patient management (e.g., smart beds).
- Manufacturing: Industrial IoT devices such as inspection cameras help with quality assessment. Manufacturers can also use temperature and humidity sensors to ensure they’re producing goods under ideal conditions.
- Retail: A common example of a retail IoT application is self-checkout machines. Other examples include smart shelves, security tags and digital price tags.
- Agriculture: For efficient and optimized agriculture, people in the industry use automated irrigation systems, weather-monitoring systems, soil-moisture sensors and remote animal monitoring, among others.
- Homes: From smart refrigerators to smart TVs, blenders, thermostats, lighting, motion sensors and HVAC systems, there are many examples of IoT devices in the home, most of which are geared towards home automation.
Advantages of IoT
Advantages of the IoT include informed decision-making, increased productivity, reduced operating costs, safety and automation. The IoT provides these benefits in the following ways:
Risks and Challenges in IoT
The risks and challenges associated with the IoT include cloud security, privacy, internet dependence, data needs and high costs.
How Should Businesses Use IoT?
Businesses can use the IoT for predictive maintenance, informed decision-making, supply chain management, personalized customer experience and automation. Businesses can use the following methods to approach IoT implementation:
- Predictive maintenance: IoT sensors can monitor and analyze the integrity of machines and other equipment used in your business. With the data they collect, the sensors can predict impending defects, alerting you to fix them before they materialize or become severe.
- Informed decision-making: IoT data offers businesses insights they can use to make decisions. For instance, end-user IoT devices can offer insights about customer behavior, which can help you decide how to react to changes in customer patterns.
- Supply chain management: Using IoT sensors and trackers, businesses can monitor goods in the supply chain. Sensors collect and process data that provides insight about inventory, driver availability and shipment tracking so businesses can deploy resources in a way that avoids waste and ensures availability.
- Personalized customer experience: IoT devices collect all kinds of data about their users, including personal data. With the collected data, businesses can infer customer preferences and use the IoT to tailor their services to each customer.
- Automation: Businesses can automate repetitive tasks with the IoT, freeing up human resources for non-automated tasks. This will optimize resource usage and enhance the effectiveness of human resources.
Final Thoughts: What Is the Future of IoT?
Just like smartphones and computers have become global, IoT devices will eventually be present all around the world, from businesses to public places and private homes. We’ll also see enhanced security and deeper integration of the IoT with AI and machine learning.
What was your first experience with the IoT? What was the device? In what way has the IoT streamlined your work? Share your experience of the IoT with us in the comments. As always, thank you for reading.
FAQ: Internet of Things in Simple Terms
The Internet of Things is a network of physical objects that aren’t regular computers.
Examples of the IoT include autonomous vehicles, smart thermostats and smart traffic lights.
The main idea of the Internet of Things is to connect physical objects (non-computers) to the internet.
The purpose of the Internet of Things is real-time data collection, data processing and response.


