What Is IBM Cloud?
What is IBM Cloud? International Business Machines (IBM) owns the cloud provider IBM Cloud, which offers public, private and hybrid cloud services. This guide delves into its features, services, use cases, benefits and drawbacks.
While it doesn’t have the same level of circulation as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud is currently one of the top 10 cloud computing platforms in the world. Its services cover the three main cloud delivery models and deployment models — IaaS, PaaS and SaaS — making it useful for various purposes.
Like Oracle Cloud, IBM Cloud is known for having extensive enterprise support, but there’s more to it than that. Read our IBM Cloud guide for more information about its features, services, use cases, benefits and drawbacks.
What Is IBM Cloud?
International Business Machines (IBM) owns the cloud computing platform IBM Cloud, a technology company best known for making computers. It is primarily a public cloud infrastructure, so its services are generally available over the internet. That said, it also offers private cloud, hybrid cloud and multi-cloud deployments.
With over 170 products, IBM Cloud’s core services include Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solutions such as IBM Cloud Object Storage, IBM Cloud Virtual Server for VPC, and IBM Cloud Network Security.
Its Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) catalog features services like IBM Analytics Engine and Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud. Finally, its Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings include IBM Cloud Container Registry, as well as Security and Compliance Center.
IBM Cloud Features
IBM Cloud offers services across 15 categories, including compute, storage, databases, quantum computing and analytics.
- Compute: IBM Cloud’s compute services offer virtual servers and bare metal servers, which you can configure and customize for all kinds of purposes and workloads. For accelerated computing, you can also get GPU servers.
- Storage: IBM Cloud provides three main types of in-cloud storage: object, block and file storage. It also has storage dedicated to backup and recovery.
- Databases: You can get structured and unstructured databases on IBM Cloud. That said, most of its database services are managed, leaving you with relatively fewer database administration responsibilities.
- Quantum computing: IBM Cloud’s quantum computing features include software development kits and runtimes for quantum workloads.
- Analytics: The platform’s analytics tools include data warehouse, data integration suite, data storage and platforms for building analytics applications.
- Automation: IBM Cloud offers automation tools for a vast range of operations, including DevOps, network and business operations.
- AI and machine learning: These tools allow you to create AI and machine learning models, as well as build apps. That said, a good chunk of them are used for speech and language.
- Blockchain: Currently, IBM Blockchain Platform is the service’s sole blockchain offering. It is a blockchain software development kit developed on Hyperledger Fabric.
- Containers: IBM Cloud provides many container-related services, including a registry, orchestration service, hosting and serverless container platform.
- Integration: If you need messaging APIs, tunnels and data migration tools to integrate different environments or app components, IBM Cloud’s extensive integration catalog includes services like IBM MQ on IBM Cloud and IBM API Connect.
- Developer tools: IBM Cloud has various developer tools. These include IBM Cloud Schematics for infrastructure provisioning using Terraform templates, along with IBM Cloud Continuous Delivery for DevOps pipelines.
- Internet of Things: The platform’s Internet of Things (IoT) services include IBM Maximo Application Suite for remote monitoring, plus IBM Edge Application Manager for automated edge computing operations.
- Observability: The observability section has several logging and monitoring tools. There’s also IBM Cloud Pak for Watson AIOps, which analyzes logs and monitoring data while offering optimization recommendations.
- Networking: With IBM Cloud’s networking services, you can create, run and manage public and private virtual networks in the cloud. IBM Cloud’s networking tools also include physical networking services such as IBM Cloud Direct Link.
- Security: The service has security tools like encryption services and IBM Key Protect for IBM Cloud, as well as compliance management services like Security and Compliance Center. It also includes firewalls, security assessment tools and a secrets manager.
IBM Cloud Deployment Models
IBM Cloud is primarily a public cloud platform, but it also supports private cloud, hybrid cloud and multi-cloud deployment models.
- Public cloud: Through its public cloud model, IBM Cloud allows users from all over the world to access its services remotely over the internet in a shared environment.
- Private cloud: IBM Cloud offers bare metal and cloud services in a dedicated environment. With the bare metal servers, you get dedicated hardware in the IBM Cloud data centers, while cloud services like IBM Cloud VPC allow you to create a logically isolated and private environment in the public cloud space.
- Hybrid cloud: You can integrate on-premises and edge computing environments with your public cloud environment. Examples of IBM Cloud’s hybrid cloud solutions are IBM Cloud Satellite and IBM Cloud for VMware Solutions.
- Multi-cloud: When setting up a multi-cloud environment, you can choose to combine IBM Cloud’s public cloud services with products from other cloud vendors such as AWS, Google Cloud and Azure.
What Is IBM Cloud Used For?
IBM Cloud is used for many purposes, including infrastructure provisioning, backup and recovery, cloud migration, machine learning, data science, software testing, software development and data analysis.
The platform’s use cases span various industries, such as government, academia, finance, healthcare, gaming, telecommunications and retail. In these industries, both IT and non-IT professionals utilize IBM Cloud services.
IBM Cloud Advantages and Disadvantages
IBM Cloud’s advantages include security, enterprise support, pricing and a strong AI focus. Its disadvantages involve limited global coverage, higher complexity, incompatibility and poor support.
Benefits of IBM Cloud
- Security: IBM Cloud offers a decent catalog of security services, including encryption, compliance, authorization and authentication tools.
- Enterprise support: With its strong focus on enterprise solutions, IBM Cloud helps meet the business, compliance and security needs of various regulated industries.
- Pricing: Aside from its default pay-as-you-go pricing, IBM Cloud offers flexible pricing options, including discounts for subscriptions and long-term commitments.
- Strong AI focus: IBM Cloud’s AI involvement is very strong, and many of its services are powered by AI.
Drawbacks of IBM Cloud
- Limited global coverage: IBM Cloud doesn’t have the same level of global coverage as top providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure.
- Higher complexity: Setting up the workflows for some of its services can be complicated.
- Incompatibility: It can be tough to integrate IBM Cloud’s solutions with third-party services.
- Poor support: Users have recently reported having negative experiences with support, citing complaints about being redirected to bots.
What Are IBM Cloud Paks?
IBM Cloud Paks are a group of packaged software solutions you can use across many cloud providers and infrastructure, partly because they are containerized. They come with pre-integrated data and are AI-driven, so they enhance automation and get processes up and running faster.
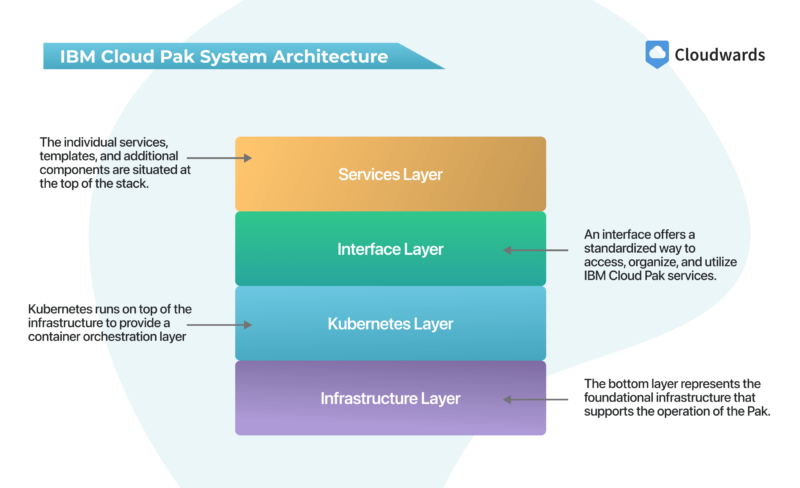
Examples of IBM Cloud Paks include IBM Cloud Pak for Data, IBM Cloud Pak for AIOps, IBM Cloud Pak for Business Automation, IBM Cloud Pak for Integration, IBM Cloud Pak for Network Automation and IBM Cloud Pak for Applications.
IBM Cloud Pricing: Is IBM Cloud Free?
IBM Cloud doesn’t have a free tier; like most public cloud providers, it uses pay-as-you-go pricing by default.
Other methods include Enterprise Savings Plans and IBM Cloud Reservations. Enterprise Savings Plans give discounts if you commit to a specified spending amount, while IBM Cloud Reservations offer cheaper rates for compute capacity commitments spanning one or three years.
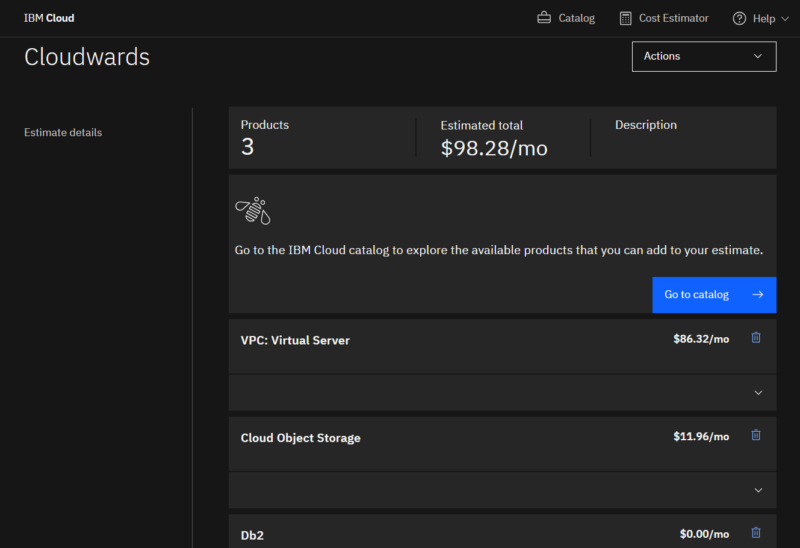
Besides the paid plans, IBM Cloud offers a 30-day free trial with varying service credits for different services. Moreover, it has always-free services such as IBM Watson Studio, IBM Cloud App ID and IBM Cloudant. While those services are free to use, you will be charged if you exceed the imposed limits.
Market Share: How Does IBM Cloud Compare to Other Cloud Computing Providers?
IBM Cloud is not one of the big three cloud providers by market share — that goes to AWS (30% market share), Azure (21% market share) and Google Cloud Platform (12% market share). Next is Alibaba Cloud (4% market share) and Oracle Cloud (3% market share). IBM Cloud ties in sixth place (2% market share) with Salesforce and Tencent Cloud.1
Final Thoughts
IBM Cloud is a top choice for enterprises, particularly those looking for AI-powered services and solutions. The various developer tools it offers are also great for IT professionals. The platform’s main drawback is its relatively limited global coverage.
Based on your experiences, which provider would you choose over IBM Cloud for AI solutions? Is IBM Cloud’s global coverage a limiting factor for you? Tell us what you think in the comments below. As always, thanks for reading.
FAQ: IBM Cloud Computing
IBM Cloud offers services like infrastructure provisioning, cloud security and data analytics.
Now a part of IBM Cloud Code Engine, IBM Cloud Function was a serverless solution that executed codes in response to events.
IBM Cloud is a hyperscaler cloud that supports public, private and hybrid cloud deployments.
IBM Cloud supports various services and products across the 15 categories mentioned above. Popular among them are Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud, IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service, IBM Watson Studio, IBM Power Virtual Server and IBM Cloud Pak for Data.
IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud both offer extensive enterprise support. That said, IBM Cloud focuses more on artificial intelligence and machine learning, while Oracle Cloud is stronger on the database front. IBM Cloud has 170 service offerings with coverage in 20 countries, while Oracle cloud offers over 150 solutions with coverage in 25 countries.


