Latency vs Speed: What Makes a VPN Fast?
Latency vs speed: what’s the difference, and what does it mean for your time on the internet? We show you how to tell these two crucial metrics apart and how to optimize both for your best online experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Latency and speed are different things. Latency refers to how quickly your online device can communicate, while speed measures the amount of data it can download or upload at a time.
- Bandwidth and speed are not synonyms. Bandwidth is your highest possible download rate, while speed is your actual download rate.
- Latency is most important for online gaming, while speed is most important for streaming. Both are useful for browsing and video chatting.
- To improve your latency (lower is better), use closer servers, get fiber-optic or cable internet, use a wired internet connection and get an up-to-date router. Avoid high-latency satellite internet connections.
Everyone wants fast internet. Whether you’re buying an internet plan or choosing an app that might affect your system resources (like an antivirus or virtual private network), speed is likely to be a top consideration. If you’re the sort who likes to do a lot of comparison shopping, you may be wondering how to distinguish latency vs speed.
Latency and speed are metrics that determine how “fast” your internet connection can run. Speed is further split into two measures, upload speed and download speed. If you want to optimize your Ethernet or WiFi network connection, you’ll need to get all three numbers to their best ranges.
This article will tell you the difference between latency and speed, the tasks for which each metric matters most and how you can use this information to get the fastest internet possible.
-
10/10/2022 Facts checked
Rewrote this guide on speed vs latency.
Latency vs Speed: What Does It All Mean?
Latency and speed are two ways of measuring how fast data moves. Both are important but it’s easy to get them confused. To explain them, let’s start by defining our terms.
Protect Your Privacy. Get Our Free VPN Guide Now!

- Comprehend the essential role a VPN plays in safeguarding your digital life
- Gain a deep understanding of how VPNs function under the hood
- Develop the ability to distinguish fact from fiction in VPN promotions
Latency is a length of time. It measures the time it takes for a connected device to make a request and receive a response. This round-trip time is also called a ping and is measured in milliseconds (ms).
Speed is a capacity. It measures how much data your device can download or upload at once. Speed is measured in megabits per second (Mbps). Download speed is the rate at which your device can receive information from another server, while upload speed is the rate at which it can send that information.
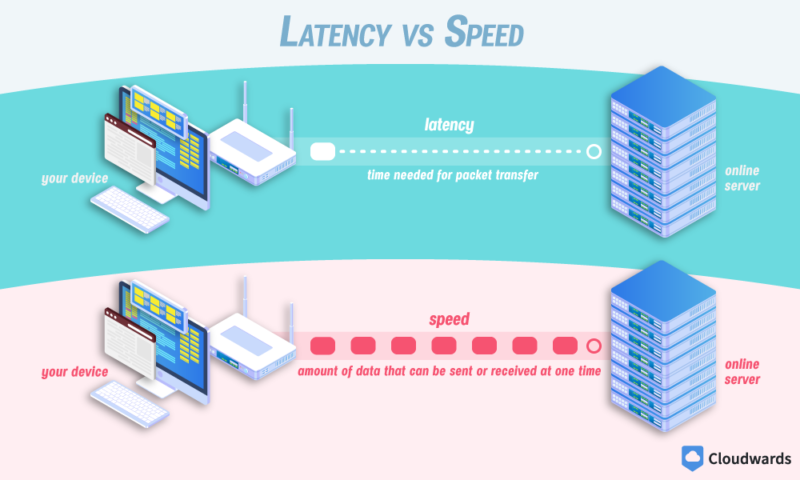
At this point, you might be wondering why there’s a difference. It seems like both are about how fast data moves on your internet connection. However, that’s not quite right. Let’s explain with a quick analogy.
Picture a highway. The amount of vehicle traffic the highway can carry at one time is determined by the number of lanes. That’s its speed, a term internet service providers often use interchangeably with network bandwidth (see “Is Internet Speed Connected to Bandwidth?” below).
A car driving on the highway represents internet latency — the time it takes to travel from one location to another. Even if a system has the capacity to move huge amounts of data, it might still appear slow if its latency is high (bad). A six-lane highway won’t do you much good if you have a slow car.

It can be confusing. The thing people usually call “speed” is more about the potential for speed, while “latency” — which sounds like a measure of inaction — is the actual measure of speed. Just remember, you need a wide road and a fast car to move quickly.
Is Internet Speed Connected to Bandwidth?
To oversimplify: Maximum bandwidth determines how much data your internet connection can move at one time, while speed is the amount of data it is moving. Bandwidth and speed are extremely similar measurements, and they’re often used interchangeably. Read our bandwidth vs data rate guide rate to learn more.
Think about our highway again. Most highways have speed limits, but when driving on the highway, you don’t often get to go the speed limit. You might manage it if there’s no traffic, but with a lot of other cars on the road, you’ll always travel a little slower than the road allows.
That slowdown represents high latency. On highways, the problem might be heavy traffic, accidents or road construction. On a website, issues might include an overloaded server, downtime or poor data distribution.
There’s another reason speed is different from bandwidth: Origin servers and destination servers don’t always allow the same maximum speeds.
If your maximum bandwidth is higher than that of the server you’re connecting to, you’ll have to work at the lower speed. In the analogy, imagine it as the difference between your car’s theoretical max speed and the actual speed limit and conditions of the road.
ISPs use bandwidth numbers in their ads instead of speed because that’s the number they can control. If someone offers to sell you 50 Mbps of “internet speed,” they’re usually referring to bandwidth — actual speed is out of their control, since it relies partly on your hardware and that of your destination server.
Is Higher Internet Latency Better Than Lower Latency?
No, this is backwards. Latency is like a golf score: You want it to be low. A shorter ping is better, since low latency means your device can exchange information more quickly.
Suppose you’re playing Overwatch and an opponent is shooting at you. Naturally, you’d want to get that information from the game server in the shortest time possible. Lower latency is your goal.
Ping vs Latency
You might sometimes hear latency described as a “ping” or “ping rate.” There’s no difference between these terms. A ping helps with measuring latency by sending a small data packet from one server to another and back. The faster the ping returns, the lower your latency.

Note that the ping rate you get from online speed tests will normally be lower than your actual ping rate. Latency depends on the other servers as much as your own modem, and distance plays a major role. As with speed and bandwidth, don’t assume that your best possible latency is what you’re actually getting.
What Does Latency Do for Your Internet Connection Speed?
Latency doesn’t affect your internet connection speed directly, but it can make your connection feel much slower. As latency is the time it takes for a signal to travel between two computers, high latency introduces a lag between when you try to do something and when the server receives it.
Some server latency is inevitable. No signal can move faster than the speed of light, so traveling between servers will always take a nonzero amount of time. Distance is one of the main culprits behind high latency — the farther away an object is, the longer it takes to communicate with it.
Latency tends to depend on more than basic physics, though. For example, a website’s servers might be overloaded with network congestion, forcing all connections into a queue for service. Insufficient network hardware on your end, or on the internet routers between you and your destination server, can also cause a high-latency connection. VPN encryption also plays a role.
In this section, we’ll run down the effects of speed and latency on several common online activities. This might help you diagnose any connection problems you’ve suffered lately. If you’re concerned about your internet speeds, our article on good internet speed has you covered.
1. Gaming
Latency is a vital metric for online gamers, who might be more concerned with their pings than with any other stat. Since most online games don’t require you to continuously download much data, you can game online with a download speed of as little as 5 Mbps and an upload speed as low as 3 Mbps.

Most of the exchanges that govern online gaming — the controller inputs, player communications and world state updates — require low latency, not high speed.
If your connection latency is too high, you’ll start to notice lag — the game state updating without making you aware of it. In fast-paced games like Fortnite, it’s common to die while waiting for your modem to catch up with the game server.
(On the other hand, some hardcore gamers have figured out how to cheat by intentionally increasing their own latencies, using the lag to make their movements erratic and unpredictable. This is what’s known as a pro gamer move.)
Gaming latency depends on more than just your home connection speed. It’s also determined by your distance from the game’s servers. Some online games come with an option to check your latency in the game. When you compare this number to the latency you get from a test site like speedtest.net, the game almost always has higher latency.
2. Browsing
Basic web browsing requires high bandwidth, high speeds and low latency, though none as high or low as the more complex tasks demand. If your speeds are low, you’ll see web pages struggling to load, and video and audio elements lagging.
High latency causes a different issue. The web page loads quickly, but it’ll feel sluggish and unresponsive. Clicking an interactive element takes several seconds to make anything happen. This isn’t as fatal as it is with gaming, but it’s still quite annoying.
3. Streaming
Streaming is the opposite of gaming. Good latency isn’t that important, but you desperately need faster speeds.
Unlike with gaming, where player input controls the state of the world, streaming is a passive download — you receive information from the streaming platform’s servers. The faster you can download that data, the better your streaming quality will be.

If your download speed is too slow for streaming, it’ll manifest as heavy pixelation (reducing the video quality to match your lowered speed) or repeated pauses as your browser banks chunks of the video and audio to play once they arrive.
4. Video Chat
Video chat requires your speed and latency to be in a good place. High latency means you’ll get out of sync with your chat partners, getting voice and video at the wrong times. Low download and upload speeds will interfere with quality, producing blurry video and robotic audio.
Tips for Improving Your Network Latency
Whether you’re a gamer, a casual browser or a remote worker who spends your day in Zoom calls, you’ll benefit from low latency. Here are a few tips to get a shorter ping.
Get Fiber-Optic Internet
Fiber internet connections provide the shortest latencies, with numbers as low as 10-15 ms. If fiber isn’t available in your area, cable-based internet has the second-lowest latency. Stay away from satellite internet connections, where the trip from the surface to orbit and back inflates ping rate to around 600 ms. Learn more in our fiber optics statistics article.
(As a side note, the Starlink broadband satellite network seems to be faster, having gotten latencies down to as low as the 40s. It’s still quite a bit slower than a terrestrial connection, though.)
Use a Wired Internet Connection
Wireless connections are more convenient for most of us, but they also add an extra step between your device and your signal’s destination. An Ethernet cable gets your web address requests to your internet service provider a lot faster, granting lower latencies and better speeds at the same time.
Upgrade Your Router
Every new generation of routers is capable of better speeds and lower latencies. If you’re using an old router, you’re not just limiting yourself to low tech, but you’re making your computer and modem work harder to make up the difference. Make sure you have a unit with router settings that can handle the speeds and latencies your modem makes possible.
Use Closer Servers
Anytime you’re in a position to choose which server to connect to — such as with a virtual private network (VPN) or an online game — pick one as close to your physical location as possible. The lower the distance, the lower the latency. A remote server’s location can cause latency all by itself.
For more tips, check out our full article on how to speed up your internet connection.
Final Thoughts: Speed vs Latency
Knowing the difference between latency and speed makes it significantly easier to optimize your internet connection. No matter what you use the internet for, diagnosing problems for yourself is a critical skill, as is knowing the steps to fix them.
We hope this article has set you on a course to a faster, smoother online experience. If you have questions about latency or speed that we didn’t answer, ask away in the comments. Thanks for reading!
FAQ
Latency, or ping, means the time it takes for your device to communicate with other devices. A longer latency leads to a longer lag time to complete actions online.
The higher your latency, the longer it takes for you to receive updates to your game state, including the movements of other players. This can be a big problem in games that rely on quick reflexes and fast action.
Gaming and video chatting are easiest, with a latency under 100 ms. Lower is better — if you can get below 10 ms, you’ll enjoy a lightning-fast internet connection.



