AWS S3 Backup Strategy: Amazon Simple Storage Service Guide
An optimal AWS S3 backup strategy starts with evaluating and understanding the types of data in your workloads. With that figured out, you can tailor your strategy to suit your use case.
Your AWS S3 backup strategy is one of the most crucial parts of your overall data protection policy. It can make or break your ability to resist permanent data loss and get back up and running in the wake of a system failure.
In this guide, we offer tips for crafting a working Amazon S3 strategy to back up data. We cover details like data selection, backup frequency, security and compliance, backing up from S3 to other cloud computing platforms and restoring your S3 backup.
-
04/12/2025 Facts checked
This article was rewritten with information on how to craft an S3 backup strategy.
Amazon S3 Backup Options
While AWS Backup is the primary tool for Amazon S3 backups, S3 versioning and cross-region replication offer some level of redundancy. Outside of AWS, S3 backup options include Clumio, Veeam and Cohesity.
Native AWS Services & Tools
Using native AWS services and tools for your S3 backup strategy offers seamless integration and potential for optimized data storage costs. It also ensures centralized management and integrated access control. Here’s an overview of some native AWS S3 backup tools:
- AWS Backup: AWS Backup is a managed service that automates and centralizes backups across AWS services.
- S3 versioning: S3 versioning is an Amazon S3 feature that allows you to retain a copy of different versions of an object.
- Cross-region replication: Cross-region replication is one of two forms of live replication on Amazon S3. It creates copies of objects in S3 buckets across different regions.
Third-Party Solutions
Third-party solutions offer specific enhancements for S3 backups. Some offer simpler user interfaces, while others have enhanced recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Below is a list of several third-party S3 backup solutions:
- Clumio: Clumio is a platform owned by Commvault. It offers data resilience across various AWS services, including Amazon S3.
- Veeam: Veeam offers backup and recovery for various AWS services, including S3, Amazon DynamoDB and Amazon RDS.
- Cohesity: Cohesity offers various solutions for cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure and Google Cloud. Its AWS backup solution works for Amazon S3, Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS.
AWS Backup Pricing Explained
Pricing for AWS Backup is primarily based on usage volume: you pay for the amount of storage used for backup, the amount of data restored and the size of the data transferred across regions. Beyond that, you may also pay for backup search, restore testing and AWS Backup Audit Manager (if you use it for backup evaluations).
AWS Backup offers restore across three tiers: warm storage, cold storage and item-level restore. However, of the three, only warm storage restore is available for Amazon S3.
In addition, AWS Backup offers four backup options:
- Warm storage — backup vault
- Cold storage — backup vault
- Warm storage — logically air-gapped vault
- Cold storage — logically air-gapped vault
However, only the two warm storage options are available for S3.
AWS Backup uses logical air gapping, which is practical for backing up AWS services. However, if you prefer the more secure physical air gapping, you can opt for a third-party alternative to AWS Backup.
Alternatives to AWS Backup
Some alternatives to AWS Backup include Veeam Backup & Replication, Cohesity and Clumio.
1. Veeam Backup & Replication

Veeam Backup & Replication is a backup service compatible with various cloud and on-premises services, including Amazon EC2, Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS. It offers immutable backups, platform-agnostic restores, AI-driven monitoring, security and compliance, and cost control.
Veeam Backup & Replication offers a free trial and three paid plans, including Foundation, Advanced and Premium.
The Foundation plan offers only backup and recovery, while the Advanced plan offers backup, recovery, monitoring and analytics. The Premium plan offers features from the Advanced plan plus recovery orchestration, which fosters robust, automated recoveries. One drawback of Veeam Backup & Replication is that there’s no standardized pricing.
2. Cohesity
Cohesity DataProtect offers an immutable backup service suitable for all kinds of platforms: in-cloud, edge and on-premises. It boasts rapid recovery times while offering a simplified, integrated management interface.
Cohesity DataProtect excels when it comes to security, offering an intelligent threat detection system and multiple layers of security features, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control and single sign-on (SSO).
Cohesity DataProtect comes with a 30-day free trial that offers a 5TB limit plus every feature of its Standard tier. The Standard tier has a fixed cost per unit, a 30-day retention period and a minimum contract period of 12 months. If you want a custom retention period, you can reach out to Cohesity for a quote.
3. Clumio

Clumio offers an autonomous backup system for services such as Amazon S3, RDS, EC2, EBS and Microsoft 365. It has a simple user interface and is mostly managed, making it appear somewhat serverless.
Data backed up on Clumio is immutable and air-gapped with security features for encryption, authentication and access control. You can restore your data across regions and accounts.
Clumio offers simpler pricing than AWS Backup, with features across three tiers for Amazon S3: SecureVault Standard, SecureVault Archive and Backtrack. It also offers a cost-optimization tool to help you minimize how much you spend on backups.
Crafting Your Backup Strategy
The success of your backup strategy depends on the careful assessment of factors like which data to back up, recovery objectives, backup frequency, security and compliance, and data sensitivity. After assessing these factors, you’ll have a better overview of what you need for a robust backup system.
Below, we’ll go over some of the crucial factors to consider when crafting your backup strategy, highlighting why you need to assess them and what to do after your assessment.
Data Selection and Determining Backup Frequency
Backing up all the data in your S3 bucket might not be an efficient strategy since larger backups are more expensive and slower to restore and back up. Moreover, some data isn’t critical, so you can afford to lose it since you can readily recreate it.
Therefore, when coming up with a backup strategy for your S3, focus on selecting only essential data. Examples of essential data include financial records, personally identifiable customer information, configuration files and employment records.
Apart from data selection, determine the backup frequency of every object to be backed up and ensure your backup platform offers backup frequencies that align with your requirements.
Better still, opt for a platform with flexible backup frequency and recovery point objectives. You can choose to run periodic backups, continuous backups or a combination of both, depending on your needs.
Assessing data access patterns is also crucial, as it can guide your choice between a hot or cold backup.
Security and Compliance Considerations
When developing an S3 backup strategy, consider data sensitivity. Sensitive data in your S3 bucket should retain the same level of security on the backup platform or even higher. In other words, if you had encryption, access control and other security measures for the live data, you should implement these security protocols and more for the backup.
In addition to security, consider the compliance and regulatory requirements that apply in your industry and location.
For instance, if you intend to handle card payments, the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a global regulatory requirement in the payment industry. In addition, if you handle data of individuals in Europe, you must comply with the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
These compliance requirements are not limited to live data, but also extend to backups. Therefore, when configuring your backup strategy, every necessary regulation must be satisfied.
Implementation and Recovery
Implementing backup and recovery for S3 using AWS Backup requires certain permissions and policies to ensure security and compliance. Then, to ensure robustness, activate S3 versioning. Let’s create and restore an S3 backup as practice.
How to Create an S3 Backup
To create an S3 backup on AWS Backup, you need to activate some S3 features and grant permissions to the role you’ll use for the backup.
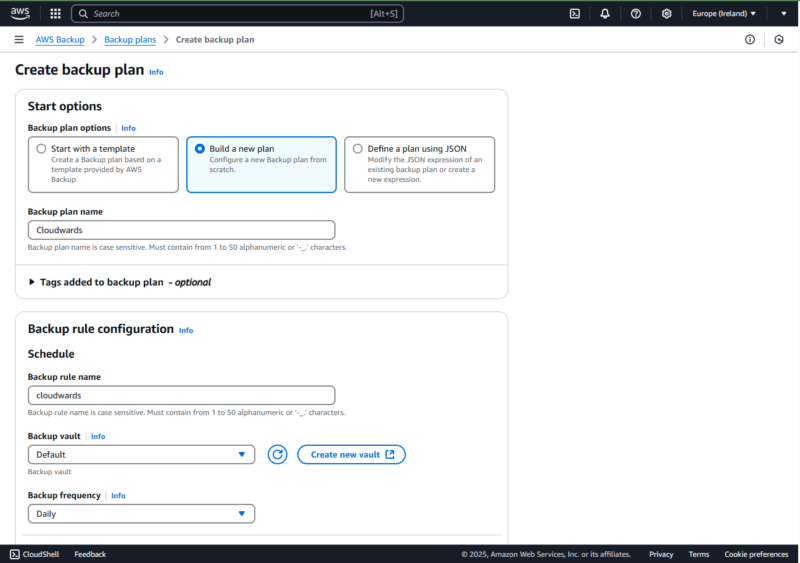
- Create a Backup Plan
To back up S3 to AWS Backup, start by creating a backup plan. Provide a backup planname and a backup rule name, then adjust the backup rule configuration as needed. You can craft your backup plan from a template that AWS Backup offers or build a custom plan.
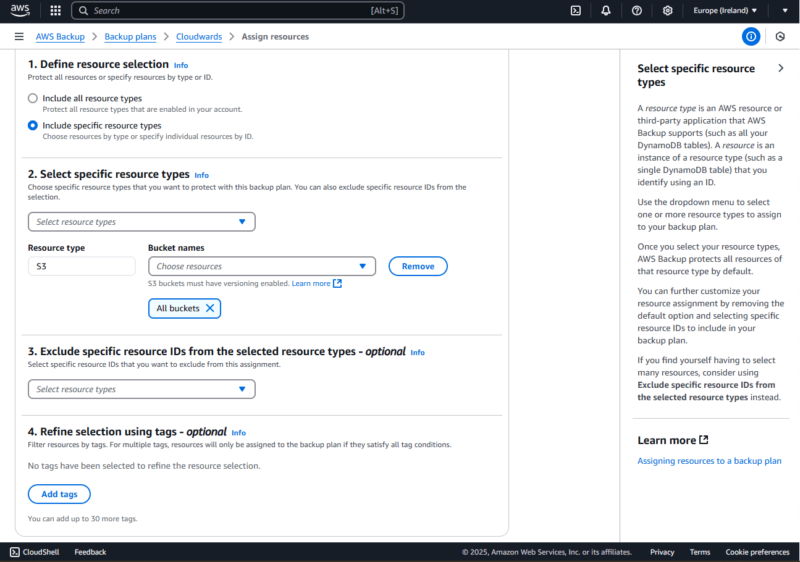
- Assign Resources to the Backup Plan
After creating the plan, provide a resource assignment name and then assign the S3 resources you want to back up to it.
You have the option to assign all the resources in your account — even non-S3 resources. Similarly, you can assign only S3 buckets: either all the buckets in the backup plan’s region at once or a single bucket.
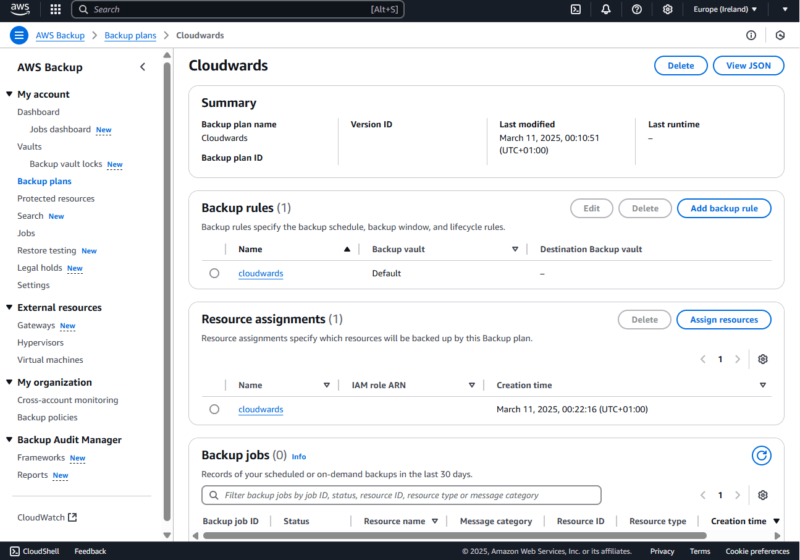
- Manage Your Backup
After assigning resources to your backup plan, AWS Backup will start backing up the resources based on the backup rule configuration. You can manage your backups from the AWS Backup dashboard, view backup jobs and external resources, conduct restore testing and much more.
Restoring Your AWS S3 Backup
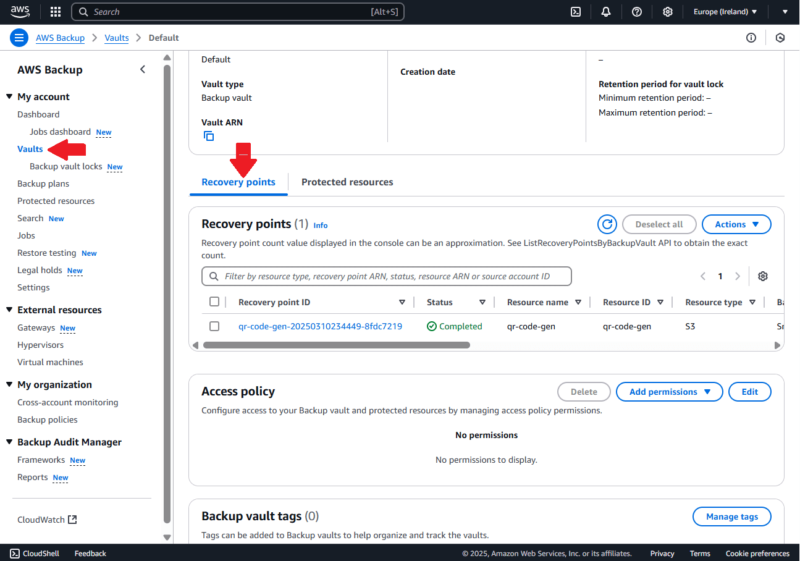
You can restore your AWS S3 backup from the AWS Backup dashboard in the “vaults” section.
- Choose the Backup Vault and Your Recovery Point
To restore your backup, choose the appropriate backup vault and select your preferred recovery point from the list. After choosing your recovery point, click on the “restore” button on the page that appears next.
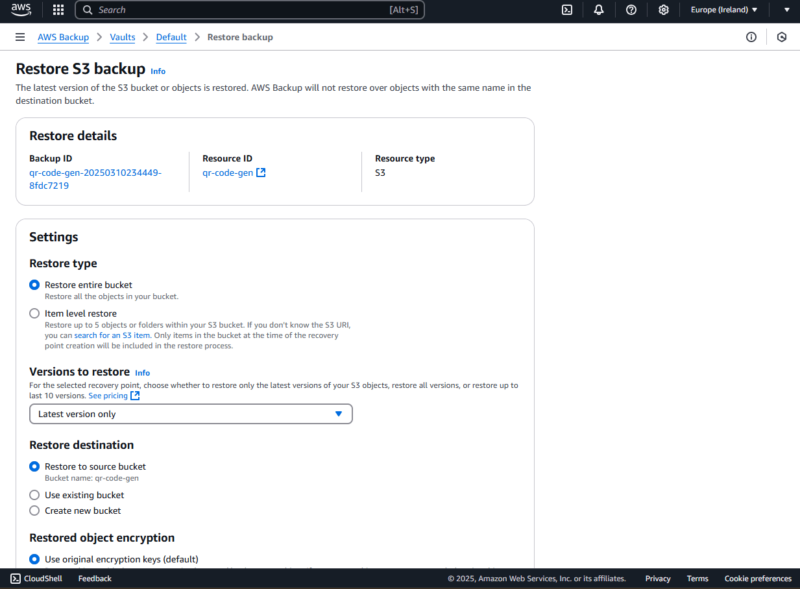
- Configure the Restore
After clicking on “restore,” you will be redirected to another page, where you can configure the restore type (bucket-level or object-level), the versions to restore, the restore destination, the restore encryption and the IAM role. When you’re done configuring the restore, scroll down and click on the “restore backup” button to complete the restore.
AWS S3 Backup Best Practices
The following best practices contribute to a robust AWS S3 backup strategy. Integrate them into your plan for the best results.
- Use multiple security layers — including encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based access control and immutability — to ensure data protection and integrity.
- Leverage Amazon S3 backup features, such as S3 object versioning and cross-region replication, for an even more resilient backup in addition to using backup tools.
- Understand and classify data to ensure you back up data in different classes as often as needed.
- Use S3 lifecycle policies to automate data transfer across S3 tiers. This will help you optimize cost and performance — infrequently accessed data stored in a cold S3 storage class is cheaper, while frequently accessed data stored in hot storage performs optimally.
- Set up a monitoring and alerting system to detect and notify you of backup failures and unusual activity. You can also create a logging system to record backup activity, ensuring you have better insight.
Final Thoughts
The key to a resilient Amazon S3 backup strategy lies in crafting an all-encompassing plan featuring robust security and compliance, well-defined recovery objectives, properly classified data and thorough testing and monitoring.
How would you improve your current S3 backup strategy? Have you used AWS Backup or third-party alternatives? If so, which option offered the best experience? Share your thoughts with us in the comments. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: S3 Bucket Backup
An AWS backup strategy is a blueprint that ensures your data and applications are protected by creating immutable copies in isolated environments.
Amazon S3 itself does not have automatic backup, but you can automate S3 backups using AWS Backup.
The 3-2-1 data backup strategy involves keeping three copies of data on two different storage types while keeping one copy off-site. If you don’t have multiple options for backup, data could get lost if one fails.

