Google Cloud Platform Security: Definition, Shared Responsibility, Products and Benefits
When choosing a cloud provider, security is a key consideration. Can you trust Google Cloud Platform to keep your data safe? Read on as we examine Google Cloud Platform security in detail, discussing its security tools, shared responsibility model and compliance with essential standards.
Google Cloud Platform security involves measures to protect data, applications and infrastructure within Google’s cloud services. This includes encryption, identity management, migration tools and network security controls.
Both Google and its customers share responsibilities for security, with Google securing the infrastructure and customers managing their data and applications. For a broader overview, read our Google Cloud review.
The framework includes products like Cloud IAM and Google Cloud Armor, which are aimed at enhancing security. These tools help mitigate risks associated with cyber threats; however, their effectiveness largely depends on users correctly implementing and managing them to avoid data breaches and unauthorized access.
What Is Google Cloud Platform Security?
Google Cloud Platform security (GCP security) encompasses all of the security tools, compliance measures and best practices that Google implements for its cloud computing platform. It’s designed to protect all the information and operations that run on Google’s cloud services. For a bird’s-eye view of how it all works, check out our Understanding Cloud Security article.
Google Cloud security covers everything from the physical servers in data centers to the data traveling across the network and the applications running in the cloud. Major parts that need security include the computers that process information, the locations where data is stored, the networks that connect everything and the software applications that users interact with.
GCP security is essential because it helps keep sensitive data safe from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, ensures that services are always available and complies with legal requirements for data protection. This is important for businesses that store and manage their information in the cloud, as strong security helps prevent data theft and loss.
What Is a Shared Responsibility Model in GCP?
The shared responsibility model in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) describes how security duties are split between Google and its customers.
Google secures the cloud’s infrastructure, including its physical buildings and software systems. Customers, on the other hand, must protect their own data and manage the settings of the cloud services they use. This division of responsibilities helps ensure that both Google and its customers actively contribute to keeping the cloud environment secure.
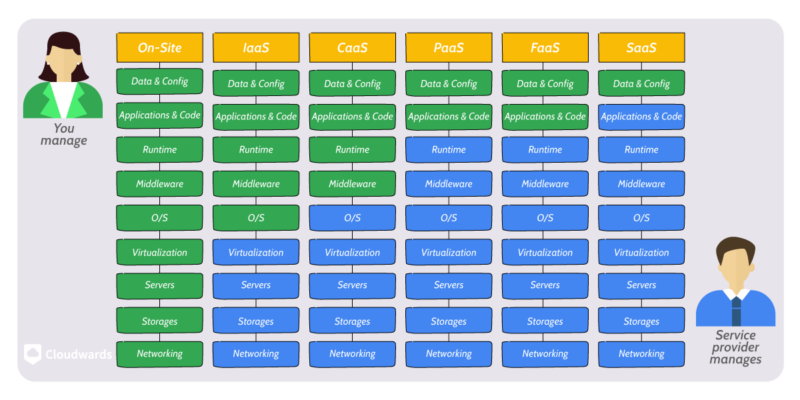
service models.
Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure security in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) refers to the protection of physical and virtual components that support cloud services. Infrastructure security in GCP covers multiple layers, ensuring comprehensive protection of cloud services.
These infrastructure layers are:
- Low-level infrastructure: This includes physical components like data centers, servers and networking hardware. Google secures these with physical protections and security protocols.
- Service deployment: This layer involves the software and systems that deploy and manage cloud services. Security measures are applied to ensure these systems are reliable.
- Data storage: This covers the storage systems where data is kept. Encryption and other security measures are used to protect stored data.
- Internet communication: This includes the networks and connections that transfer data over the internet. Security measures are implemented to prevent unauthorized access.
- Operations: This involves the ongoing management and monitoring of all the above layers. Continuous monitoring and security checks are used to maintain infrastructure safety and functionality.
Customers can fulfill their responsibility by securely configuring and managing their data and applications. They should use GCP products like Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for network isolation, Cloud Security Scanner for vulnerability detection and Cloud IAM to control permissions.
Not properly implementing these measures can lead to data breaches, unauthorized access and service disruptions. These risks can lead to significant security incidents and impact business operations.

Network Security
Network security in GCP entails the measures taken to protect data as it travels across networks, such as securing data in transit, ensuring network isolation and protecting against external threats. GCP secures the underlying infrastructure, such as data centers and global networks, and provides tools and services to secure data as it moves across the infrastructure.
Customers, on the other hand, are tasked with configuring and managing their own network security settings. They can use Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create isolated network environments, Cloud Armor for protection against DDoS attacks and Cloud VPN for secure connections between on-premises networks and GCP.

networks within the Google Cloud Platform.
Application Security
Application security refers to the measures taken to protect applications running in the cloud from threats. It involves securing the application code, managing access and protecting against vulnerabilities. GCP provides a secure infrastructure and tools to help developers build secure applications, such as automatic security updates for managed services and security monitoring.
Platform-as-a-Service products like App Engine GCP handle security tasks like patching and system maintenance. Customers must secure the app code, configure security settings and regularly update their applications. They can use Cloud Web Security Scanner to detect vulnerabilities, Cloud IAM to control access and reCAPTCHA to prevent bots and abusive acts.

Software Supply Chain Security
The software supply chain is the entire process of developing, building and deploying software applications, including all components, tools and services involved. Software supply chain security in GCP ensures the integrity and security of software from development through deployment, covering all phases of the software development life cycle (SDLC).
Software supply chain security in GCP is a shared responsibility, with Google providing tools like Software Delivery Shield and customers implementing secure practices. Key GCP products include Cloud Build, Artifact Registry and Binary Authorization for secure CI/CD pipelines and container management.

Customers must configure these tools, implement secure coding practices and manage access controls. Neglecting supply chain security can lead to vulnerabilities through compromised dependencies or unauthorized code changes, potentially resulting in data breaches or system compromises.
Data Security
Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption or theft throughout its life cycle. In Google Cloud Platform (GCP), this involves safeguarding data both when it is stored (data at rest) and while it is being transmitted (data in transit) through encryption and secure communication protocols.
Google provides built-in encryption services and tools like the Cloud Key Management Service for encryption key management and Persistent Disk for data storage security. Customers are responsible for implementing their own security measures, such as setting appropriate access controls and managing encryption keys. Tools like Cloud IAM can help control access to data.
Some of the encryption methods Google Cloud offers include the following:
- Customer-supplied encryption keys (CSEK): Customers provide their own encryption keys, which Google uses but does not manage or store long term.
- Cloud Key Management Service (KMS): This allows customers to manage and rotate encryption keys themselves within Google Cloud’s infrastructure.
- Cloud Hardware Security Module (HSM): This offers a secure environment for customers to manage cryptographic operations using dedicated hardware.
- Cloud External Key Manager (EKM): This lets customers manage encryption keys outside of Google’s infrastructure using supported external key management services.

by encoding information at rest and in transit.
Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies that ensures users have appropriate access to technology resources.
It involves the identification, authentication and authorization of users and systems within the Google Cloud environment. Google Cloud provides the IAM framework and tools that facilitate secure and granular access control through services such as Cloud Identity, Cloud IAM and Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP).

and resources based on user identity and context.
Customers must configure and manage access controls to ensure users have the right level of access to resources. This responsibility includes applying the principle of least privilege, which dictates that permissions should be limited to only what is necessary for users to perform their tasks.
The following security risks may emerge if these IAM policies are not properly configured:
- Over-privileged users: Users with excessively broad access can unintentionally or maliciously harm resources.
- Stale accounts: Outdated user credentials can provide an entry point for attackers if not promptly deactivated.
- Misconfiguration: Incorrectly configured IAM policies can lead to unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Endpoint Security
An endpoint is any device that connects to a network, such as a computer, smartphone, server or tablet. Endpoint security in cloud computing involves protecting these devices from cyber threats as they access Google Cloud services and data.
In GCP, the endpoint is a shared responsibility. Google’s role in endpoint security involves providing tools and technologies that help protect the devices that access its cloud infrastructure, ensuring they are safeguarded against cyber threats.
Some tools that GCP provides include Cloud Endpoints and BeyondCorp Enterprise. However, it’s up to customers to ensure their devices are protected when they connect to Google Cloud. Capabilities include setting up secure network environments via virtual private clouds (VPCs), keeping security software updated and teaching users about safe online behavior.

Security Monitoring and Operating
Security monitoring and operating refers to the continuous process of overseeing and managing a network’s security posture by tracking, analyzing and responding to security threats and vulnerabilities to protect data and resources.
Google provides the infrastructure and tools necessary for continuous security monitoring and threat detection within its cloud environment. This includes automated security assessments and real-time threat detection services.
These GCP monitoring and operating tools include:
- Google Cloud Security Command Center: This offers a comprehensive view of the security status of cloud resources, enabling customers to detect and respond to threats.
- Cloud Logging and Cloud Monitoring: This allows customers to collect, view and analyze security logs from across Google Cloud services.
- Google Cloud anomaly detection: This automatically detects unusual activity that may indicate a security threat.

Platform resources to detect and investigate potential threats.
Customers are responsible for configuring these tools to suit their specific security needs, actively monitoring their own environments and responding to alerts. They must also establish their own security operations protocols to manage and mitigate incidents.
The following security risks could emerge without proper monitoring:
- Undetected threats: Without effective monitoring, some security threats might go unnoticed, potentially leading to data breaches or compromised systems.
- Delayed response: Inadequate monitoring can result in slow responses to security incidents, increasing the damage caused by attacks.
- Insufficient data analysis: Failure to properly configure and use monitoring tools can lead to gaps in security data analysis, hindering effective threat detection and response.
Governance, Risk and Compliance
Governance, risk and compliance (GRC) in cloud computing refers to the set of practices and processes used to ensure an organization’s IT operations align with business goals and adhere to regulatory requirements. It involves managing the risks associated with cloud environments and ensuring all cloud activities comply with both internal policies and external laws.
Failure to comply can lead to these risks:
- Non-compliance fines and penalties: Failure to comply with relevant regulations can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
- Data breaches due to inadequate policies: Without proper governance and risk management, organizations might face increased vulnerabilities, leading to potential data breaches.
- Reputation damage: Non-compliance and poor governance practices can damage an organization’s reputation and trustworthiness.
What Are the Different GCP Security Products and Solutions?
The main GCP security products and solutions are Google Cloud Armor, Chronicle Security, Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS), Cloud IAM, Cloud Security Command Center (Cloud SCC) and VPC Service Controls. These products offer specific features designed to enhance the security of GCP.
- Google Cloud Armor: This protects against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and acts as a web application firewall. It uses Google’s infrastructure to keep applications available during attacks. Its security policies, customizable rules and real-time threat visibility help maintain application performance by stopping threats early.
- Chronicle Security: Chronicle Security is a tool for managing and analyzing security information. It offers log management, threat detection and threat intelligence. It helps GCP by providing a clear view of security events, enabling quick responses to incidents and effective threat management.
- Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS): Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) manages cryptographic keys for cloud services. It includes key creation, rotation, destruction and import, with centralized management and audit logs. KMS secures data on GCP by ensuring strong encryption to protect sensitive information.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM controls who can access GCP resources and the actions they can perform. It provides detailed access control and policy management, ensuring only authorized users can access specific resources and thus enhancing security.
- Cloud Security Command Center (Cloud SCC): Cloud SCC is a platform for managing and monitoring security across GCP. It provides visibility into assets, vulnerabilities and threats, helping to secure GCP by offering insights for proactive security management.
- VPC Service Controls: VPC Service Controls creates security boundaries around GCP resources to prevent data leaks. It allows security policies to be set to control resource access. This helps secure GCP by limiting unauthorized access and keeping data within defined boundaries.
What Are the Different Third-Party Cloud Security Tools for GCP?
The main third-party cloud security tools for GCP are Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet and Trend Micro.
- Palo Alto Networks: Palo Alto Networks offers tools to protect against threats in GCP. It includes features like intrusion prevention, firewall management and automated security actions. This helps keep GCP secure by stopping threats in real time and managing firewalls effectively.
- Fortinet: Fortinet provides security solutions such as firewalls and VPNs. Features include threat protection, secure VPN access and centralized management. Fortinet helps secure GCP by protecting against cyber threats and ensuring secure access to cloud resources.
- Trend Micro: Trend Micro offers security for cloud environments. It includes workload protection, container security and threat detection. This helps secure GCP by protecting applications and data from vulnerabilities and detecting threats.
What Are the Benefits of GCP Security?
The main benefits of Google Cloud security are better data protection, easier compliance, better threat detection and lower costs.
- Better data protection: GCP encrypts data when it’s stored and when it’s in transit. This makes it harder for hackers to steal or read your data. For example, if someone tries to intercept your data while it’s being transferred, they wouldn’t be able to make sense of it because it’s encrypted.
- Easier compliance: GCP offers tools to help with regulatory compliance. These features can assist with meeting various data protection standards, such as HIPAA and the GDPR. For instance, the platform provides logging and auditing capabilities that can be useful for demonstrating compliance with certain regulations.
- Better threat detection: GCP includes systems for identifying potential security issues. These use data analysis to spot unusual patterns that might indicate a problem. An example is detecting multiple failed login attempts, which could signal an attack attempt.
- Lower costs: By including security features in its core offering, GCP may reduce the need for separate security tools. This could potentially lower overall IT security expenses for some organizations. However, the actual cost savings would depend on each organization’s specific needs and existing infrastructure.
What Are the GCP Security Risks?
The main GCP security risks are misconfiguration, data breaches, insider threats and compliance violations. These risks can potentially compromise the data integrity, system availability and overall security posture of organizations using Google Cloud Platform services like Compute Engine.
- Misconfiguration: Incorrect setup of GCP settings or features can lead to unintended public access to private data, improper access controls or disabled security, which could expose information or lead to unauthorized access to cloud resources. A Thales study found that misconfigurations caused 31% of recent cloud security data breaches.
- Data breaches: Data breaches involve unauthorized parties gaining access to sensitive information. For Google Cloud security, this could be due to cloud infrastructure or user application vulnerabilities. A 2023 IBM report found that 82% of all data breaches involved cloud-hosted data. This could lead to data loss, or financial or reputation damage.
- Insider threats: Insider threats are risks from individuals within an organization who have legitimate access to GCP resources. Potential consequences include data theft, cloud resource sabotage or unintentional exposure of sensitive information. This highlights the importance of managing security at the user level.
- Security and compliance violations: This risk involves failing to meet regulatory requirements for data protection and privacy. It can occur due to improper data handling or insufficient security and compliance measures, and lead to legal penalties, fines and loss of customer trust. Thus, cloud environments need robust compliance management.
What Are the Best Practices for Securing Google Cloud?
The best practices for securing Google Cloud include implementing strong access controls, encrypting data, regularly updating and patching systems, engaging in monitoring and logging activities, and implementing the principle of least privilege. These practices form the foundation of a strong cloud security strategy for GCP environments.
- Use strong access controls: This involves setting up strong authentication and authorization for cloud infrastructure. Examples include enabling MFA for all accounts, using Cloud IAM to manage administration identities and control user permissions, and regularly reviewing access policies for Google Cloud projects.
- Data encryption: Encryption protects data in cloud storage from unauthorized access. Google Cloud provides built-in encryption for data at rest and in transit. Consider using customer-managed encryption keys for sensitive data in your cloud infrastructure.
- Regular updates and patching: This practice keeps all systems and security tools up to date. Always enable automatic updates where possible, regularly check for and apply security patches, and maintain a systematic update approach across all Google Cloud resources.
- Monitoring and logging: This involves tracking activities within your Google Cloud environment. Use the cloud provider’s built-in logging tools, set up alerts for suspicious activities and regularly review logs to detect potential security threats.
- Implementing the principle of least privilege: This principle limits user access to only what’s necessary for their tasks. Implementing this principle entails regularly auditing user permissions, removing unnecessary privileges and using role-based access control to ensure users access only the resources they need for projects in Google Cloud.
Final Thoughts
Securing your Google Cloud resources is a shared responsibility between you and GCP. By understanding your role in this model, you can take proactive steps to protect your data and applications.
Using tools like Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Cloud Security Command Center will help you boost security. Regular audits, continuous monitoring and following best practices are important for maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Did you find our GCP security guide useful? Have you applied any of the security practices we discussed? Which GCP security tools have you found effective? We’d love to hear about your experiences in the comments below. Thank you for reading!
FAQ: GCP Security
Google Cloud Platform is highly secure, offering advanced security features, continuous monitoring and compliance with industry standards.
The GCP security model involves a shared responsibility between Google and its customers, ensuring comprehensive security coverage.
To stay safe on Google Cloud, implement strong access controls, encrypt data, regularly update systems and continuously monitor for threats.
Google Cloud provides various security tools, such as Identity and Access Management (IAM), Cloud Security Command Center, VPC Service Controls and Cloud Armor.

