eSIM vs Physical SIM: Pros, Cons, Signal Strength & Security Compared
eSIM technology is expected to grow in the coming years. You might be wondering whether eSIMs are really better than physical SIMs, or whether eSIMs are better for security and privacy because they’re embedded. In this eSIM vs physical SIM comparison, we explore the differences and the pros and cons.
You’ve packed your bags and are ready to set off traveling. Suddenly, panic strikes as you realize you forgot to activate a roaming plan for your destination country and might be hit with a costly bill. Having multiple physical SIMs is a hassle, but an eSIM could be a solution. In this article, we’ll break down the main differences between eSIM vs physical SIM cards.
Physical SIMs have been around since 1991. These small chips that you insert into your device exist to authenticate the device to a mobile network. This enables you to make calls, send short messages and access the internet. They can also store contact information, which allows you to easily access your contacts when you switch to a new phone.
eSIMs were introduced in 2010 for the IoT (short for Internet of Things) industry. They were then slowly introduced to the telecommunications market through new devices like the Google Pixel 2 in 2017; the iPhone XR, XS, and XS Max in 2018; and the Motorola RAZR in 2019. However, it wasn’t until 2022 that eSIMs started to make an impact in the telecommunications industry.
Though both physical SIMs and eSIMs serve the same function, there are some differences that make one more preferable than the other in certain situations. The following sections take a look at the pros and cons, connectivity and security differences of each service. Read our best eSIM for international travel guide if you’re ready to pick one.
How Are eSIMs & Physical SIMs Different?
| eSIM | Physical SIM | |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase Process | Available for online purchase and activation | In-store purchase or online delivery |
| Activation | Activated digitally | Needs to be inserted into a device |
| Carrier | Reprogrammable to various carriers | Usually locked to a specific carrier (some multi-carrier SIM cards exist, like Eminify, but they are rare) |
| Device Transfer | Transfer procedure dependent on your carrier | Easy to transfer to a new device |
eSIMs and physical SIMs differ in how they are purchased, set up and managed. eSIMs are purchased online and activated digitally. With physical SIMs, you can buy them in person at a carrier store or order them online with delivery. eSIMs are embedded into the device, which makes them more secure and harder to lose. Physical SIMs have evolved over time, becoming smaller and more prone to loss.
Transferring your physical SIM to a new device takes just a few minutes, but eSIM transfer can be easy or difficult depending on your carrier. For example, if you need to factory reset your iPhone, you might need to contact your carrier and ask how to reactivate the eSIM. The process can also differ if you’re making a switch from iPhone to Android or vice versa.
Smartphones these days are generally equipped with one or two physical SIM card slots. This means that if you use physical SIMs, you can use only up to two carriers at once.
While this holds true for eSIMs as well (you can use only two eSIMs simultaneously), they still offer greater flexibility, as you can download up to eight eSIMs on your phone. This allows you to manage your travel, work or personal profiles separately all on one device by simply deactivating and activating different eSIMs.
Pros and Cons: eSIM Card
Embedded SIM cards offer a number of benefits and drawbacks. Though entirely dependent on your use case, it’s easier to figure out whether you should make the switch to an eSIM when you know both sides of the coin.
Pros
- More secure: With eSIMs, you don’t need to worry about SIM cloning if your phone is stolen or lost. SIM cloning happens when a fraudster gains access to your SIM, clones it and uses it to carry out criminal activities.
- Convenience: Whether you’ve purchased a new phone or are traveling to a new country, you can activate eSIMs in an instant. Do a quick search online about which network providers offer eSIM data plans in your destination country. Having multiple eSIM profiles is convenient when you’re planning to visit more than one country.
- Sustainable: Unlike traditional plastic-and-metal SIM cards that are difficult to recycle, eSIMs are significantly smaller in size and are embedded while the phone is being made. This reduces the number of SIMs being manufactured, packaged and shipped to global destinations, and reduces waste from discarded physical SIMs.
Cons
- Limited device compatibility: As eSIM technology has made considerable growth only in the past few years, your options are limited to the latest smartphones on the market. This means that if you own an older phone model such as a Samsung Galaxy S20, iPhone 10 or Huawei P50 Pro, you won’t be able to use eSIMs.
- Your mobile carrier has more control: If you fail to configure your eSIM properly or encounter other technical issues while activating it, you might need to contact your mobile carrier. Depending on the quality of the carrier’s service, the process of resolving issues can delay you.
- Switching phones can take more time: If you want to disable your eSIM and reactivate it on a new device, it may take a while compared to simply physically transferring your SIM card to the new phone’s physical SIM slot.
Pros and Cons: Physical SIM Card
Since traditional SIMs have been around for a while, we may have naturally developed a preference for them over eSIMs. However, as the telecommunications world is continually advancing, it’s important to take a look at their drawbacks as well.
Pros
- Easy to activate: A regular SIM is ready to use as soon as you insert it into a device’s SIM card slot. There’s no need to scan a QR code or make configuration changes in order to activate it.
- Device switching: Physical SIM cards offer more convenience, as they can be easily transferred from one device to another.
- Better privacy: Depending on your carrier’s policies, physical SIMs offer better privacy, as you have direct control over what you want to do with them. You can remove, replace or destroy them whenever you want.
Cons
- Vulnerability: If your physical SIM card is lost or stolen, you may face challenges recovering your phone number or the data within the SIM.
- Inconvenient to switch carriers: If you want to switch carriers, you need to physically change the SIM card. That means visiting a store to purchase a new SIM, or ordering the SIM online and waiting for delivery.
- Physical SIMs might phase out: Wireless carriers are turning to eSIM technology as more phone models are adapting to support eSIMs. With the way the wireless industry is progressing, traditional SIMs might soon become obsolete.
eSIM vs Physical SIM: Signal Strength
eSIMs and physical SIMs do not have control over how much signal your phone has. Smartphones have antennas inside them that are used to transmit and receive radio waves from cell towers, and the antenna quality can affect signal strength.
Generally, though, signal strength has more to do with your carrier’s coverage. The more cell towers there are in your area, the higher your chances are of getting a better signal. Other factors that affect signal strength include, but are not limited to, physical obstructions, environmental conditions and network load.
Physical SIM vs eSIM: Security
Probably the most obvious advantage of eSIMs over traditional SIM cards is that they are embedded into your device, reducing the risk of physical theft. Traditional SIM cards are more vulnerable to tampering attacks when they fall into the wrong hands.
Contacting your carrier to deactivate your traditional SIM can take a while, but many eSIMs come with mobile apps and adequate support that can help disable eSIM profiles online almost instantly.
Though both a physical SIM and an eSIM are susceptible to SIM swap attacks and port-out frauds, an eSIM has more security advantages — it can be programmed remotely and can rely on stronger verification systems.
Nonetheless, it’s important to be aware of the best practices to keep your data safe and secure. You can do this by:
- Choosing reputable network providers
- Setting up a SIM card lock with a SIM pin
- Using encryption to protect sensitive information
- Subscribing to eSIM services that have apps equipped with tools, tutorials and 24/7 live chat support
Physical SIM vs eSIM for Travel
If you’re looking for a travel SIM, eSIMs offer more convenience and value than physical SIMs. In some countries, buying a physical SIM card can be time-consuming, especially if you’re not familiar with the local network providers and their plans. You can research this in advance, but you may struggle to find the provider’s booth when you arrive in the country.
Sticking to your national carrier’s roaming plans can cost you more money since, in a way, you’re “renting” another country’s infrastructure and services. Your home provider doesn’t manage the foreign network’s rates, so roaming fees can get expensive.
eSIMs are a more cost-effective alternative since they are sold in prepaid packages for specific countries, giving you the flexibility to pay only for what you need. eSIMs also offer the convenience of being able to activate multiple data plans, which gives travelers extra flexibility when visiting different countries.
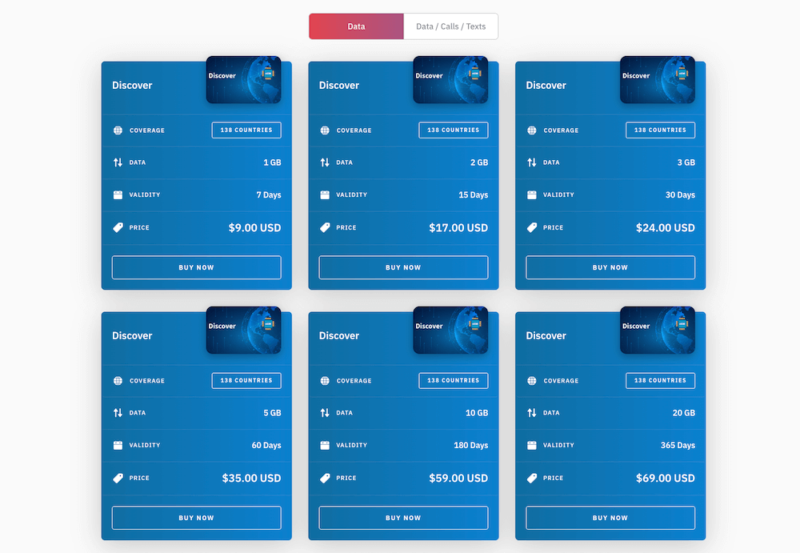
138 countries, as well as specific region plans.
To stay extra safe, though, it’s best to consider using an eSIM alongside a VPN. Read our Saily eSIM review and NordVPN review to check out some of the best security products that parent company Nord Security offers. You can also refer to our best VPN guide for more alternatives.
What Is an iSIM?
A more advanced form of eSIM is called “integrated subscriber identity module,” or iSIM. Whereas a physical SIM can be removed from a device and an eSIM is embedded by being soldered into a device during manufacturing, an iSIM is directly integrated into one of the main components of a smartphone, called a “system-on-chip” (SoC).
iSIM vs eSIM
Some of the differences between iSIM and eSIM technology include the following:
- eSIMs are currently more widespread in the telecommunications industry, whereas iSIMs are geared more towards the IoT.
- Unlike eSIMs, which require a small chip to be soldered into a device, iSIMs are integrated into a phone’s main processor, which allows devices to be more compact. This can be beneficial for industries such as healthcare.
- With iSIMs, manufacturers can produce smaller devices that require less power consumption, optimizing production costs and sustainability.
Is My Phone Compatible With eSIM?
To check whether your phone supports embedded SIMs, go to your device’s settings. Check whether the phone is locked to a certain carrier, and whether your cellular settings allow you to add eSIMs. This process may vary depending on the type of operating system you have and the device model.
How to Check iOS eSIM Compatibility
The first step is to go to “settings” > “general” > “about” > “network provider lock.” If it shows “no SIM restrictions,” then your phone is unlocked and your phone can switch carriers. The second step is to go to “settings” > “mobile service” and see if it says “add eSIM” under the list of active SIMs. If it does, then your iPhone supports eSIMs.
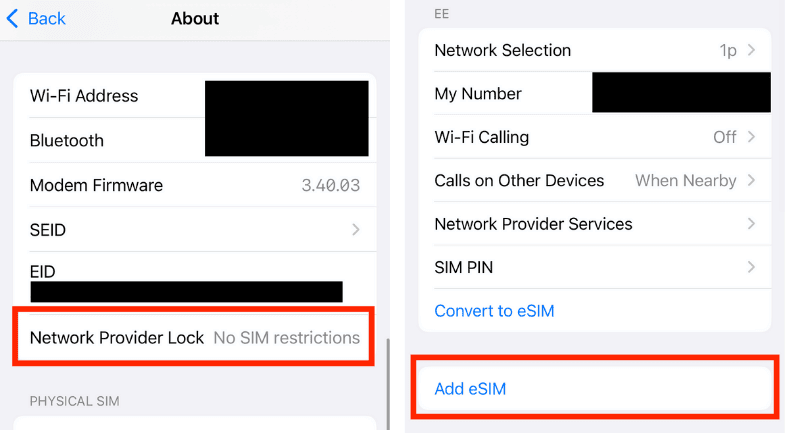
it is eSIM compatible.
How to Check Android eSIM Compatibility
First, go to “settings” > “connections” (or “network and internet”) > “SIM card manager” > “mobile networks” (or “cellular “networks”) > “network operators.” If you can search for different mobile operators, your phone is most likely unlocked. If it displays only one network, then it’s most likely locked.
Next, check if your Android is eSIM enabled. Go to “settings” > “connections” > “SIM manager.” If it shows “add eSIMs,” then your device supports eSIMs.
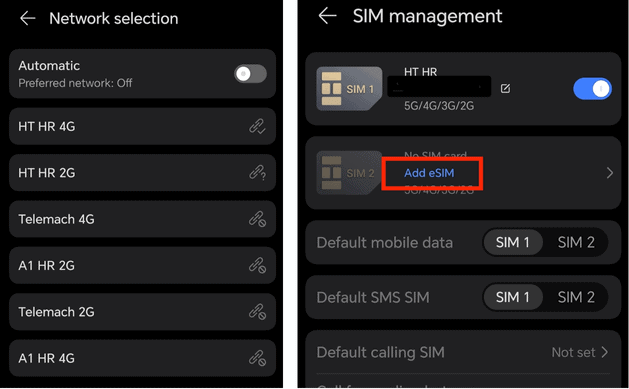
List of eSIM-Compatible Phones
Here are some eSIM-enabled phones currently on the market:
- iPhone XR
- iPhone XS
- iPhone XS Max
- iPhone 11 and up
- Samsung Galaxy S20
- Samsung Galaxy S20+
- Samsung Galaxy S20+ 5G
- Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra and up
Some Samsung devices are not compatible with eSIMs based on location and carrier.
Final Thoughts
Both physical SIMs and eSIMs have pros and cons. However, as companies are continually finding ways to optimize production costs and develop more sophisticated, smaller devices, it’s easy to see that eSIMs will become more popular. In terms of security, travel convenience and sustainability, the benefits of eSIM technology are clear.
Do you plan on switching phones anytime soon? If so, are you interested in testing out embedded SIM technology? Have you already tried an eSIM? What was your experience like? Share your thoughts with us below. Thank you for reading!
FAQ: eSIM vs Physical SIM, Which Is Better?
An eSIM is better than a physical SIM in terms of physical security, travel convenience and cost, and sustainability.
eSIMs make it more complicated to switch to a new phone, as the procedure varies depending on your provider. Since your network provider also handles your personal information, there’s a risk of data breaches and other privacy issues when you travel to different countries with varying data laws.
Yes, if your phone is eSIM compatible then it’s probably worth switching to an eSIM, especially if you travel a lot. Embedded SIM technology is expected to grow in the coming years, and you can save on roaming costs while traveling by switching to country-specific eSIM plans.


