67 Cyber Security Statistics, Facts & Trends: Data on Attacks, Breaches & Threats for 2025
Globally, over 5.5 million cyber security professionals were working in the field by the end of 2022. Even though digitizing industries like gambling, retail and education came with many benefits, it also opened up new exploit routes for cybercriminals. Read on to understand the major cyber security statistics and the threat landscape that you should note.
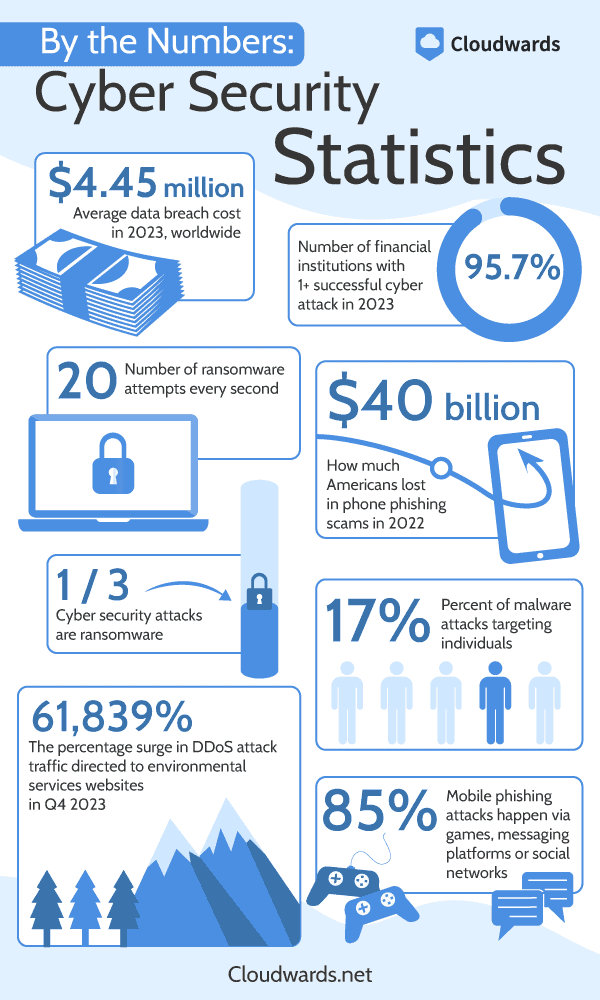
Online data security is a serious concern — there were 7.6 trillion intrusion attempts in 2023, a 20% increase from 2022.1 This cyber security statistics roundup shares some cyber security figures that can help you better understand the cyber security threats, and how industries are grappling with security breaches and the increasing risk of outside actors gaining access to sensitive information.
-
03/22/2024
We updated this statistics article to include an expert opinion on cyber attacks and the best way to protect yourself from them.
-
07/04/2024
We rewrote this article with recent statistics and a new structure.
-
04/11/2025 Facts checked
We’ve checked and updated our cyber security facts and sources for the latest information on cyber threats.
Cyber Security Statistics: General
First, let’s take a look at some general trends within the cyber security industry.
- From March 2023 to May 2023, threat actors deployed 11.5 successful attacks per minute,5 and one-third of them were ransomware.13
- State-sponsored entities like Russian APT28 and the North Korean Lazarus Group were particularly active in 2023.5
- The number of hacking intrusions has risen 613% from 2013 to 2023.1
Hacking Statistics
Hacking, or intrusion, is the unauthorized access or exploitation of networks or computer systems. Hackers have different motives and can disrupt operations, steal confidential data or manipulate systems. Today, hacking is among the major cyber security concerns, with cyber criminals mostly exploiting vulnerabilities in a system or codebase.
Statistics About Malware Attacks
Malware is malicious software designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to a network or computer system. Malware can take the form of adware, viruses, trojans and so much more. Attackers can send malware through email attachments, exploit software vulnerabilities or post malicious ads.
Protect Your Privacy. Get Our Free VPN Guide Now!

- Comprehend the essential role a VPN plays in safeguarding your digital life
- Gain a deep understanding of how VPNs function under the hood
- Develop the ability to distinguish fact from fiction in VPN promotions
Malware is malicious software designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to a network or computer system. Malware can take the form of adware, viruses, trojans and so much more. Attackers can send malware through email attachments, exploit software vulnerabilities or post malicious ads.
- 71% of malware attackers have specific targets.6
- 17% of malware attacks target individuals.13
- There were 5.4 billion malware hits globally in 20217; in 2023, there were 6.06 billion malware attacks recorded — the highest global attack volume since 2019.1
- North America recorded the largest numbers of malware attacks in 2023, with over 3.17 billion attacks, followed by Europe, with over 1.4 billion malware attacks.1
Global Malware by Region, in Millions
Phishing Attacks Statistics
A phishing attack is a cyberattack where hackers deceive users into providing sensitive data such as usernames, passwords and bank details. Hackers may execute phishing attempts using copycat websites, emails and social media platforms. Users are led to believe they are browsing legitimate websites or receiving official emails, and they end up giving data to malicious individuals.
Social engineering tactics remain the foundation of successful phishing campaigns, with attackers exploiting human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive information. The rise of deepfakes has introduced a new dimension to phishing attacks, with AI-generated voice and video content being used to impersonate executives and authorize fraudulent transactions.
- More than half of phishing attacks in 2021 were executed for identity theft.9
- Americans lost $25.4 billion in phone phishing scams in 2023.11
- Hackers execute 85% of mobile phishing attacks through games, social messaging platforms or social networks.10
Phishing Attach Methods
Statistics on Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is a type of malware attack that encrypts files and systems. The hackers usually ask for a ransom in the form of payment to decrypt such files. Hackers execute ransomware attacks using approaches like social media platforms, fake promotions and false job adverts, but there are even Ransomware as a Service options on the dark web.
- Ransomware is the top action type for breaches. This means that most attackers mainly use ransomware to achieve their goals.8
- In a SonicWall survey, two-thirds of respondents indicated that business email compromise (BEC) attacks are an area of concern.7
- BEC attacks led to $2.9 billion in losses in 2023.12
- There are almost 20 ransomware attempts every second.7
- Global ransomware attacks peaked in 2021, with over 623 million ransomware attacks. In 2023, there were over 317 million ransomware attacks.1
- Of the organizations that had their data encrypted by ransomware attackers in 2021, 46% of them paid the ransom.14
Percentage of Organizations That Paid Ransoms.
If you want to learn more ransomware stats, check out our full ransomware statistics article.
DDoS Attacks Statistics
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks involve malicious individuals sending lots of traffic to a target system or website. The attack is meant to overuse the available resources and make the site unavailable to legitimate users. DDoS attacks can slow down a system, shut it down or cause downtime.
The expansion of 5G networks is creating new attack vectors for DDoS attacks, with higher bandwidth capabilities enabling more powerful and disruptive attacks against critical infrastructure.
- Microsoft intercepted 1,955 DDoS attacks per day between mid-2021 and mid-2022.15
- Malware-based DDoS attacks are the most common threat to Linux-based systems.5
- The U.S. and China accounted for over a quarter of all the DDoS attack traffic globally in 2023.16
- There was a 117% year-over-year increase in DDoS attacks in Q4 2023.16
- There was a 61,839% surge in DDoS attack traffic directed to environmental services websites in Q4 of 2023, coinciding with COP 28, the UN Climate Change Conference.16
Statistics on Personal Data Breaches
A personal data breach is the unauthorized access or disclosure of personal data. Such breaches can lead to the alteration, destruction or loss of personal data. Cybercriminals seek confidential data like their victims’ bank account information, social security numbers and health records. You can read more data in our data privacy statistics article.
- Data breaches in the U.S. increased by 20% from 2022 to 2023.17
- Increased exploitation of vendor systems, cloud misconfiguration and new types of ransomware attacks are the major causes of the increase in personal data theft cases.17
- Over 1.5 billion records were breached in 2022.17
- Over 360 million people experienced institutional and corporate data breaches in the first eight months of 2023.17
- Globally, over 80% of data breaches involve data stored in the cloud.17
Attacks on Government Agencies
Cybercrimes targeting government agencies are common, especially on bodies governing elections, healthcare and international trade. The motives behind such attacks vary, ranging from differences in personal ideologies and money demands to getting government secrets.
Cyber Security Statistics by Industry
Hackers target different industries aiming to harvest different forms of valuable data or manipulate systems. Certain sectors, such as government agencies, finance, banking and healthcare institutions, are the biggest targets of cyberattacks. Let’s check the stats and trends for various industries.
Cybersecurity Victim Attack Categories
1. Healthcare Industry
Healthcare is one of the most important industries in an economy — and it’s also one of the most targeted. Attackers understand that the simple manipulation of healthcare systems can lead to loss of life. Thus, hospitals and those in the medical field will likely pay ransoms when such attacks occur.
- The U.S. healthcare industry had the highest cyber security breach costs at $10.93 million in 2023.19
- Data breach costs in healthcare increased by 53.3% from 2020 to 2023.19
- Hacking contributed to over 75% of the healthcare industry’s data breaches in 2023.21
- 62% of data breaches in the healthcare industry target healthcare providers.21
- 25% of the breaches target business associates in the healthcare industry, while 13% target business associates.21
2. Education
Cyberattacks in the education industry have become common recently due to an increase in online education programs. Ransomware is one of the most common attacks, where attackers ask for ransoms and threaten to delete databases. Educational platforms also carry lots of data that hackers can use for identity theft and other malicious activities.
- Cyberattacks targeting U.S. schools lead to learning losses lasting from three days to three weeks. It also takes two to nine months to recover from such attacks.22
- About 647,000 students in U.S. K-12 schools and school districts were reportedly affected by ransomware attacks in 2021.22
- Almost half of the higher education schools in the U.K. experience an attack or breach at least weekly.23
- After a cyber security incident, 61% of higher education centers experience negative outcomes, such as data or money losses.23
- Social engineering attacks accounts for 69% of the attacks that target educational institutions in the U.K.24
- In a study by the London Grid for Learning (LGfL) and the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), 83% of the schools they interviewed had experienced at least one cyber security incident.24
3. Financial Sector
Most cybercriminals are after money, which explains why the financial sector is their best target. Banks and financial institutions store a lot of personal data that hackers can use to commit fraud. Users also hold deposits in some institutions, and hackers will target such funds.
- Data breaches cost the financial sector $5.90 million in the U.S. in 2023.19
- Data breaches in the financial sector are among the most expensive to fix.19
- In the first quarter of 2022, 23.6% of all phishing attacks targeted financial institutions.18
- Blackberry Cybersecurity Solutions stopped 17,000 attacks targeting financial institutions from March 2023 to May 2023.5
4. Retail Industry
Countless transactions are happening in the retail industry. This industry processes a lot of data when customers register, order, pay and add their shipping details. Cyberattackers can target customer data, disrupt business operations and demand ransoms.
- 52% of retail businesses worldwide have a cyber strategy in place.29
- Malware is the leading cyber security threat in retail.30
- Ransomware is the second leading cyberattack in retail.30
- A data breach in the retail sector costs $2.9 million on average.28
- The online retail market was worth over $1.09 trillion in 2022.28
5. Banking
Banks process a large amount of data as they enable deposits and let customers transact on their platforms. Cyberattackers can target customer deposits or personal details to perform financial fraud. Banks are also legally obligated to ensure their users don’t engage in money laundering schemes.
- The global cyber security market size in banking was $74.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $282 billion by 2032.33
- An employee of a financial institution has access to 13% of the company’s files.25
- A typical employee of a large financial services organization can access over 11 million files.25
6. Small Businesses
Small businesses store and process lots of data that cybercriminals can use to their benefit. Unfortunately, most small businesses don’t invest in the best cyber security, making them an easy target for criminals. Social engineering, phishing, insider threats and ransomware are some of the cyberattacks that cybercriminals use to target small businesses.
- 43% percent of all cyberattacks target small businesses.32
Cyber Security Statistics by Country
Cyberattackers target different countries based on the resources that they own.
- The following are the countries and regions that had the highest average data breach costs in 2023.19
- 🇺🇸 The United States at $9.48 million
- 🇦🇪 The Middle East at $8.07 million
- 🇨🇦 Canada at $5.13 million
- 🇩🇪 Germany at $4.67 million
- 🇯🇵 Japan at $4.52 million
- The U.S. has incurred the most costs related to containing data breaches for 13 years in a row.19
- The U.K. saw a drop of 16.6% in its average data security breach costs in 2023, taking it out of the top five.19
- Japan also saw a decrease in the average data breach costs, but it wasn’t as drastic, leading it to take the U.K.’s spot in the top five.19
Cyber Security Job Statistics
Cyber security has become one of the most sought-after professions in the 21st century. Small and large businesses seek professionals to protect their business and customer data. Individuals are also being educated on how to keep their data safe by enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication, creating strong passwords and browsing safe websites.
- According to CyberSeek, findings by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) showed there were 457,433 cyber security job openings in the U.S. by August 2024.4
- By June 2023, about 1,495,825 people in the U.S. were employed in the cyber security space.4
- There is a shortage of about 4 million professionals in the cyber security industry globally.4
- Information security analysts in the U.S. were earning a median annual wage of $120,360 in 2023.31
Human Error Statistics
Some human error incidents can enable hacking. For instance, using a combination of your names as a password makes it easy for hackers to access your accounts.
How Much Does Cybercrime Cost Victims?
A cybercrime attack can cost individuals and organizations in two ways: the cost of countering the attack and the loss of revenue during the attack. Businesses hire security experts to deal with attacks and inform users of their effects. The time it takes to contain a cyberattack depends on the severity of the breach and the expertise of the professionals you contract.
Final Thoughts
Cyber threats can target individuals or organizations. Cyberattacks come in different forms, like phishing, malware, ransomware and DDoS. As organizations continue to adapt to evolving threats, implementing zero trust architecture has become a critical strategy for preventing lateral movement within networks and minimizing the impact of potential breaches. Organizations should also begin preparing for quantum computing threats, which could potentially render current encryption methods obsolete.
How individuals and organizations react will depend on the type of breach and the systems in place. Invest in cyber security if you want to stay safe online. You can also familiarize yourself with cyber insurance and take the proper precautions.
Are there some cyber security statistics or trends we may have missed? Which stats did you find compelling? What should internet users do to remain vigilant against cyber threats? Share your views in the comments sections. Thanks for reading.
FAQ: Cybercrime Statistics
Statista estimates that the global cost of cybercrime will hit $13.82 trillion by 2028.
Malware is the biggest cyber security threat today. Malware can come in different forms, such as spyware, ransomware, trojans, worms, keyloggers and more.
Data from memoori.com indicates that only 15% of all cybercrimes are reported. Most companies fail to report as they fear damaging their reputation, while others don’t know the exact steps to follow in such cybersecurity incidents.
It is estimated that there are 2,200 cyber attacks per day.
Sources:
- SonicWall — 2024 Cyber Threat Report
- Cyber Edge — Report Defense Cyberthreat
- Verizon — 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report
- ISC2 — Cybersecurity Workforce Demand/ CyberSeek
- BlackBerry — Quarterly Global Threat Report — August
- Positive Technologies — Cybersecurity threatscape: Q2 2022 / Sophos — AI Cybersecurity
- SonicWall — 2022 Cyber Threat Report
- Verizon — 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR)
- APWG — Phishing Activity Trends Report 4th Quarter 2021
- CyberNews — Mobile phishing attacks are scary and on the rise
- Truecaller Insights — The True Cost of Spam and Scam Calls in America
- FBI — IC3 Internet Crime Report 2023
- Positive Technologies — Cybersecurity threatscape: Q2 2022
- Sophos — Ransomware Hit 66% of Organizations Surveyed
- Microsoft — Digital Defense Report 2022
- Cloudflare Blog — DDoS threat report for 2023 Q4
- Apple — The Continued Threat to Personal Data: Key Factors Behind the 2023 Increase
- Phishing Activity Trends Report, 1st Quarter 2022
- APWG — Phishing Activity Trends Report 1st Quarter 2022
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights — Breach Portal
- HMP Global Learning Network — Report: Cybersecurity Threats Increasing for Healthcare Organizations
- U.S. GAO — Critical Infrastructure Protection: Additional Federal Coordination Is Needed to Enhance K-12 Cybersecurity
- UK Department for Science, Innovation & Technology — Cyber security breaches survey 2023: education institutions annex
- GDPR Blog — The worrying state of cyber security in schools
- Varonis — 82 Must-Know Data Breach Statistics [Updated 2024]
- IBM Report — Half of Breached Organizations Unwilling to Increase Security Spend Despite Soaring Breach Costs
- CISOMAG — “Psychology of Human Error” Could Help Businesses Prevent Security Breaches
- Trustwave Spiderwebs Blog — The 2023 Retail Services Sector Threat Landscape
- Grant Thornton — Cyber security concerns in the retail sector
- BRC — How Retailers Can Address the Rising Cybersecurity Threat
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics — Information Security Analysts
- University of North Carolina — Cybersecurity: A Global Priority and Career Opportunity
- Allied Market Research — Cybersecurity in Banking Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report


