What Is Cloud TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) & How to Calculate and Reduce It?
Cloud TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) is a framework that helps businesses understand the true cost of cloud adoption. Let’s find out how to maximize cost savings to align with organizational and financial goals.
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering greater scalability, flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. However, the dynamic nature of cloud pricing models, including direct and indirect costs, makes it difficult for organizations to fully understand their financial commitments. This is where cloud TCO — or Total Cost of Ownership — comes into play.
Cloud TCO helps businesses calculate the true cost of their cloud investments while factoring in direct and indirect costs. Organizations should seek to understand and optimize their cloud TCO to avoid budget overruns, maximize their cost savings and make strategic decisions that align with their financial and operational goals.
What Is Cloud Computing TCO?
Cloud computing TCO refers to the overall costs required to adopt, operate and maintain cloud services for a specific period of time. In traditional infrastructure, these costs were primarily Capital Expenditures (CapEx), whereas modern cloud computing infrastructure mostly operates on a consumption-based model based on Operational Expenditures (OpEx).
TCO includes direct cloud costs like subscription fees, storage and compute resources, along with indirect costs like migration, training and downtime. Cloud TCO is dynamic and influenced by factors such as usage patterns, pricing models and scalability. Businesses should understand cloud TCO to avoid unexpected expenses and optimize their cloud investments.
Benefits of Calculating Cloud TCO
Calculating TCO is essential for businesses looking to make informed financial and strategic decisions regarding their cloud investments. Each business should analyze its direct and indirect costs to gain a clear picture of its long-term expenditure and optimize resource allocation. Businesses will derive the following benefits from calculating TCO.
1. Enables Strategic Planning for Cloud Adoption and Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding the full cost of cloud TCO can help businesses develop strategic plans that align with their long-term goals, enabling them to allocate resources efficiently. Organizations can make data-driven decisions about which workloads to migrate, which cloud providers to use and how to allocate budgets effectively.
For example, a financial services company handling sensitive customer data may decide to adopt a hybrid cloud approach to balance security with cost-effectiveness.
2. Maximizes Cost Savings and Optimizes Cloud Expenses
Calculating cloud TCO helps identify potential areas for cost reduction, such as underutilized resources or inefficient pricing models. This leads to significant cost savings and more efficient cloud expenditure.
For example, an e-commerce company experiencing seasonal traffic spikes can leverage auto-scaling and spot instances where they can manage fluctuating demand in a cost-effective way.
3. Improves Cost Allocation and Forecasting of Total Cost of Ownership
Accurate TCO calculations aid in budget planning and forecasting future expenses. This helps facilitate better cost allocation across departments or projects, which improves accountability and transparency. For example, a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) company can use TCO data to predict how its cloud costs will grow as its user base expands.
4. Leads to Better ROI Analysis Through Calculating Cloud TCO and Indirect Costs
When businesses calculate their cloud TCO, they can assess their cloud initiatives’ return on investment (ROI) by factoring in their direct and indirect costs. Organizations can compare the benefits gained against the expenses incurred. Through TCO analysis, organizations can align their cloud investments with their business goals and deliver tangible value.
5. Leverages Cloud Cost Savings for a Competitive Advantage
Organizations that optimize their cloud TCO can reinvest the cost savings into strategic opportunities, improving profitability and enhancing their innovation and growth. By reducing unnecessary expenses, companies can offer competitive pricing, improve their quality of service or accelerate product development to gain a competitive edge in the industry.
6. Enables Effective Risk Management Through Cloud TCO Analysis and Operational Costs
Analyzing cloud TCO helps businesses mitigate the financial and operational risks associated with cloud adoption and avoid budget overruns. In addition, calculating TCO allows organizations to evaluate the implications of different cloud strategies, enabling them to choose the most suitable option.
7. Enhances Cost Transparency by Analyzing Direct and Indirect Costs
A detailed cloud TCO calculation gives a clear breakdown on costs related to cloud usage, including hidden and intangible costs. This improves transparency and accountability across teams, empowering them to make cost-conscious decisions and use their resources efficiently.
8. Provides Cloud Infrastructure and Pricing Models That Support Scalability
With a well-planned cloud TCO approach, businesses can scale efficiently without incurring excessive costs, and they can choose scalable infrastructure and pricing models that align with their goals.
Different cloud providers offer different pricing models for businesses based on their needs, such as pay-as-you-go rates, reserved instances and volume discounts. When businesses understand the impact of these pricing models, they can scale operations efficiently while maintaining financial stability.
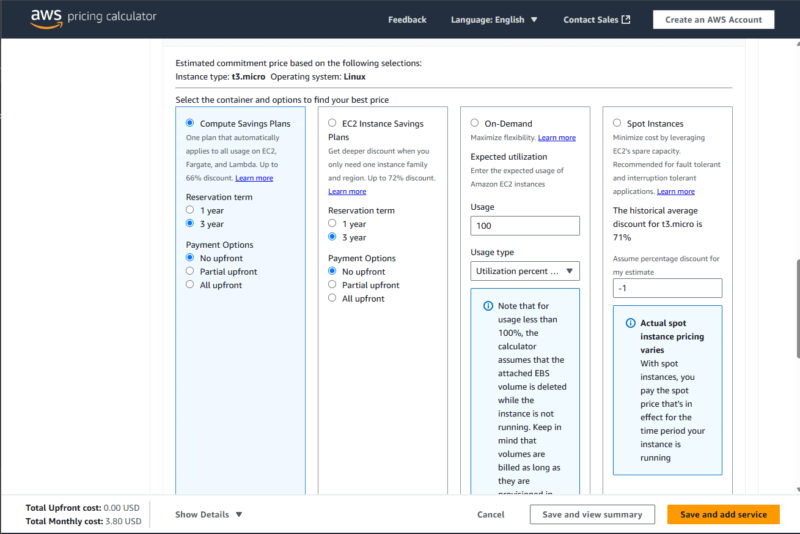
prices based on different pricing models.
9. Optimizes Cloud Service Provider Contracts Through TCO Calculations and Migration Costs
TCO calculations help organizations understand the long-term financial impact of cloud services so they can negotiate better contracts with cloud providers. Businesses can assess migration costs and determine whether it is more cost-effective to switch providers or renegotiate their existing contracts. This helps them secure the best possible financial terms for their cloud investments.
How to Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
Calculating the TCO for cloud services is crucial as it helps organizations understand the true financial impact of cloud investments. To effectively calculate cloud TCO, organizations need to account for the direct costs, indirect costs and future expenses. We will walk through the steps of calculating cloud TCO below.
1. Set a Time Frame for Calculating Cloud TCO
Cloud costs may vary over short- and long-term usage periods. Organizations may consider evaluating their TCO for a specific project, one year, three years or the entire lifecycle of their cloud adoption. Having clear time frames will provide accurate comparisons and forecasts to create realistic financial plans.
2. Track Cloud Infrastructure and Operational Costs
Organizations should document all their existing infrastructure costs, such as compute, storage and network infrastructure expenses.
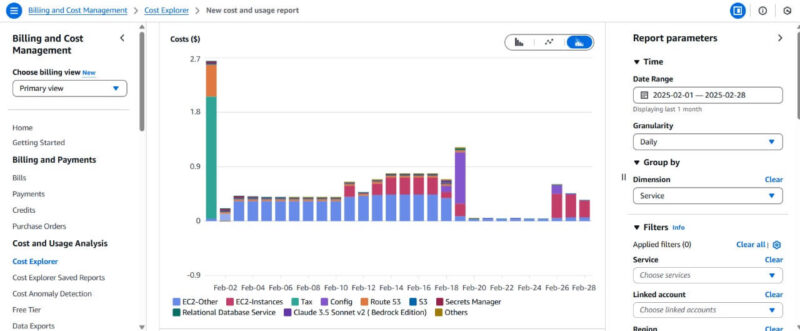
The ongoing costs vary based on usage, and you must monitor them continuously. You could use cloud provider tools like the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management to track your monthly cloud costs. Monitoring these expenses helps businesses identify cost drivers as well as their cloud deployment’s opportunity cost.
3. Measure Indirect Costs and Hidden Costs in Cloud Environments
Indirect costs include expenses such as compliance, employee training, management costs and security. Businesses must account for these hidden costs to get a true financial picture and understand the full impact of cloud adoption, helping them avoid unexpected expenses.
4. Factor In Cloud Migration Costs and Total Cost of Ownership
Migrating to the cloud incurs migration costs that you should include in your TCO calculations, such as data transfer fees, application refactoring and potential downtime. Factoring in these expenses helps businesses prevent unexpected costs, ensuring a smooth migration process.
end-to-end migrations and modernization journeys.
5. Estimate Cloud Growth and Future Expenses
Cloud costs increase as businesses scale, so it’s important to forecast future expenses based on expected growth. Organizations should consider factors that would lead to increased expenses, such as additional workloads and data expansion. This proactive approach will prepare your business for future expenses and help you scale efficiently.
6. Perform the Calculation for Total Cost of Ownership and Cost Allocation
After identifying all their costs, businesses can perform a comprehensive TCO calculation using the following formula:
Cloud TCO = Direct Costs + Indirect Costs + Migration Costs + Future Expenses
This calculation provides a comprehensive view of cloud expenses, leading to better decision-making and cost optimization. It also helps businesses understand the true cost of their cloud investment so that they can make informed decisions.
How to Maximize Cloud Cost Savings
Cloud computing can lead to unexpected costs if not managed correctly. To optimize their cloud spending, organizations must maximize their cloud cost savings. Cloud costs can quickly increase due to factors like inefficient resource usage, underutilized services and poor pricing models. Organizations can maximize their potential savings in the following ways:
Cloud TCO vs On-Premises TCO
Businesses often compare TCO for cloud computing and on-premises environments. Cloud computing offers flexibility, scalability and lower upfront costs, while physical infrastructure provides greater control and predictable long-term expenses.
By comparing cloud TCO and on-premises TCO, organizations can choose an approach that best aligns with their budget, goals and strategy. The table below compares cloud TCO and on-premises TCO based on different factors.
| Cloud TCO | On-Premises TCO | |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Costs | Low upfront costs. Uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model. | High upfront costs. Requires investment in hardware and software. |
| Operational Costs | Variable costs based on usage. Can be a monthly/annual subscription or usage-based billing. | Mainly fixed costs, such as maintenance and staffing. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; businesses pay only for necessary resources. | Scaling requires the acquisition of new hardware and infrastructure. |
| Maintenance | The cloud service provider handles maintenance. | An in-house IT team handles maintenance and upgrades. |
| Security | The cloud provider manages security under a shared responsibility model. | The organization has full control over security and may require dedicated staff. |
| Long-Term Costs | Costs fluctuate based on usage and service adjustments. | Costs become predictable over time after the initial investment. |
Final Thoughts
Businesses must understand and calculate their cloud TCO to optimize their IT spending and make informed decisions on cloud adoption. Performing a thorough TCO analysis helps them budget for their cloud spending, maximize the business value of their cloud investments, and maintain high efficiency and performance.
As cloud adoption continues to grow, businesses must take a proactive approach to cost management by leveraging cloud monitoring tools, choosing the right pricing models, optimizing resource usage and considering energy consumption.
Calculating cloud TCO is a continuous process that requires frequent evaluation and refinement. Organizations should implement the best practices for cost savings and understand their key cost drivers to best align their IT investments with their business objectives.
Thank you for taking the time to read our article. What strategies have you found most effective for managing cloud expenses? Share your thoughts with us in the comments section below and consider forwarding the article to your networks.
FAQ: Cloud Total Cost of Ownership
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is the comprehensive cost of a system over its lifetime, including initial investment, operational expenses, maintenance and indirect costs. In cloud computing, TCO helps businesses evaluate their direct and hidden costs when using cloud infrastructure, enabling them to make informed financial decisions.
Cloud computing costs vary depending on usage, service type, service provider and pricing model. Many factors affect these costs, such as compute resources used, storage, data transfers and licensing.
Indirect costs can significantly impact cloud TCO by increasing the overall expenditure on cloud infrastructure. Examples of indirect costs include training, compliance and downtime. Failing to account for them can lead to budget overruns and inefficient cloud investments.