What Is Cloud ROI? Definition, Examples, Calculation, Advantages & More
Understanding cloud ROI (return on investment) helps businesses maximize their financial and operational gains from cloud adoption. How do we measure success? Let’s explore the key factors, cloud ROI calculation and expert strategies to optimize cloud investments.
Measuring cloud ROI (return on investment) helps businesses assess the value of their cloud investments by weighing cloud costs against the benefits of cloud adoption.
The ROI metric helps businesses migrating to cloud computing platforms and those looking to optimize their cloud environment by helping them ensure their cloud expenditure aligns with their cloud budget. Keep reading to learn more about cloud ROI.
What Is Cloud ROI?
Cloud return on investment (ROI) measures the financial benefit a company derives from making cloud investments. It evaluates whether cloud adoption is worth it for an organization.
Cloud ROI considers not only the cost savings from cloud investments but also other benefits of adopting cloud-based solutions, such as improved efficiency, faster time to market and enhanced security.
It is essential for a business to understand its cloud ROI. For businesses moving to the cloud for the first time, the cloud ROI gives a clear picture of the financial impact of their cloud investment. For businesses that are already using the cloud, cloud ROI helps optimize existing cloud deployments and justify further investments.
Cloud vs On-Premises ROI
On-premises infrastructure requires heavy upfront investments in hardware and software licenses, which makes it capital expenditure (CapEx)-intensive. On the other hand, the economics of cloud computing favor a pay-as-you-go model, which shifts costs to operational expenditure (OpEx), where businesses pay only for what they use.
Cloud infrastructure offers greater agility, flexibility and innovation potential compared to on-premises servers. Cloud platforms provide access to technology features such as AI and advanced analytics that promote faster deployments.
On-premises infrastructure, on the other hand, offers greater infrastructure control and customization, as businesses own the resources and can modify them to fit their use case.
How to Calculate Cloud ROI
Calculating cloud ROI helps organizations determine whether their cloud investments are delivering value. Cloud ROI compares on-premises costs, cloud expenses and the long-term value gains from which an organization would benefit by adopting cloud infrastructure.
Calculating cloud ROI ensures businesses get the most from their investment. Follow the five steps detailed below to calculate cloud ROI, or use an ROI calculator.
1. Identify All the Cloud-Related Costs
When calculating cloud ROI, consider the total cost of ownership, including one-time and ongoing costs. One-time costs are paid once, such as migration costs and training costs. Ongoing costs are incurred regularly and include cloud service fees, maintenance and support costs, and subscription fees, among others.
2. Quantify the Benefits of Cloud Adoption
Identify the tangible and intangible benefits of moving to the cloud and compare them to maintaining on-premises infrastructure. Tangible benefits include a direct cost that is lower than current costs, such as reduced infrastructure costs, lower energy usage and pay-as-you-go savings.
Intangible benefits may not include a direct cost, so organizations have to attach a subjective value to them. For instance, let’s assume a company that used to take three days to fully launch its product to a global audience now takes three hours on the cloud to achieve the same result and start selling.
The amount of money made between the actual time of launch and the time the platform would have launched with the previous system can be evaluated as an intangible benefit to the organization due to the faster time to market.
3. Calculate the Net Benefits
Determine the benefit of the cloud investment by calculating the difference between the total benefits and the total costs of the cloud investment.
Net benefits = total benefits – total costs
4. Calculate the Cloud ROI
Calculate the cloud ROI using the following formula:
Cloud ROI = (net benefits) / (total costs) * 100
A negative ROI would mean the investment incurred a loss during the studied period, while a positive ROI would indicate that there was a net gain in the investment during the period. Sometimes, businesses may see a negative ROI in their first year due to high one-time costs such as migration and training. The ROI then improves over time.
5. Analyze and Optimize
Analyze the cloud ROI to identify areas of improvement. For example, examining trends over time can help identify declining returns.
Some strategies to improve the ROI include optimizing cloud resources, leveraging reserved instances and implementing automated scaling. Organizations should implement continuous monitoring with cost alerts to help track spending and maintain maximum efficiency.
Cloud ROI Example
For our cloud ROI example, we’ll consider a software development company currently operating an on-premises infrastructure where it hosts its website, database and customer analytics tools. The company has been experiencing performance and scalability challenges and has decided to move its workloads to AWS.
The cloud migration entails the following costs and benefits:
- Cloud migration costs:
- Cloud services: $20,000 per month
- Migration costs: $50,000 (one time)
- Personnel training: $10,000
- Cloud migration benefits (compared to the current on-premises infrastructure costs):
- Reduced server maintenance costs savings: $15,000 per month
- Increased developer productivity savings: $10,000 per month
- Faster time to market savings: $5,000 per month
- ROI calculation:
- Total annual costs: 20,000 * 12 + 50,000 + 10,000 = 300,000
- Total annual benefits: (15,000 + 10,000 + 5,000) * 12 = 360,000
- ROI: (360,000 – 300,000) / 300,000 * 100 = 20%
The company has a return on investment of 20% in the first year, so it makes sense to migrate to the cloud. To calculate the ROI in subsequent years, we should consider the costs incurred and the cloud migration benefits that the organization gains during the year.
To make business sense, a project should have a net-positive ROI over the course of the period of evaluation. The first year usually records the lowest ROI, and it may even be negative due to a huge number of initial one-time costs. In subsequent years, the ROI generally improves due to lower costs incurred.
What Are the Elements That Impact Cloud ROI?
The elements that impact cloud ROI collectively determine the financial and operational effects of cloud adoption. Businesses need to assess these core building blocks when evaluating their cloud investments. Understanding the effects of these elements on finances helps businesses make informed cloud investment decisions.
We will evaluate the following five factors that affect cloud ROI: cloud service and infrastructure costs, migration costs, scalability and elasticity, operational efficiency and productivity, and security and compliance.
1. Cloud Service and Infrastructure Costs
Cloud service costs include fees charged for services such as compute, storage, networking and databases. These costs vary based on pricing models such as pay-as-you-go and reserved instances.
Organizations should select the pricing that best optimizes their spend. For example, spot instances can greatly reduce cloud costs since they offer discounts of up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing. They are also a great choice for workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
Cloud costs can easily get out of hand if not managed properly. Idle resources, over-provisioning and lack of pricing visibility may lead to unnecessary expenses. Organizations use monitoring tools, cost management tools and automation to optimize their cloud spending.
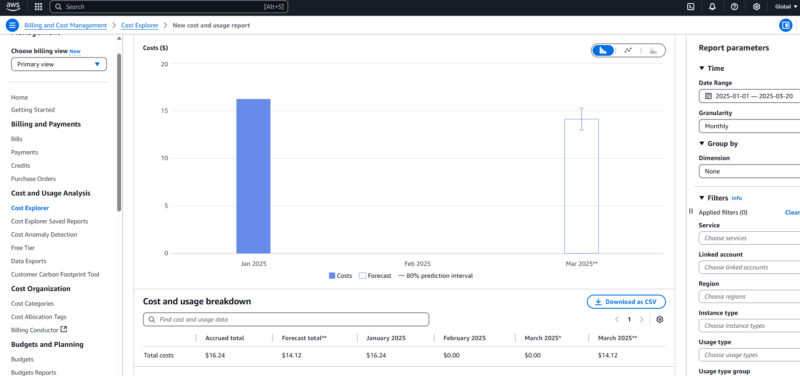
provide insights into cloud spending on AWS.
2. Migration Costs
Organizations must account for all costs associated with migration, such as data transfer fees, third-party migration tools and potential infrastructure outages during transition. The costs mainly impact the ROI in the short term, as they rack up quickly while the organization is setting up the infrastructure.
On the positive side, these costs are typically one-time expenses. Companies offset these initial investments with reduced infrastructure and maintenance costs over time. To achieve a higher ROI, businesses should plan carefully, use automated migration tools and conduct thorough testing to avoid disruptions.
3. Scalability and Elasticity
One of the biggest advantages of cloud migration is the ability to scale based on demand. This helps greatly improve the ROI, especially for businesses with fluctuating workloads. In addition, it ensures that businesses are billed only for the resources they use instead of having to pay for fixed infrastructure year round.
Businesses must properly manage and configure scalability to optimize their ROI. Overprovisioning resources can lead to wasted spending, while underprovisioning may lead to a resource shortage during peak times, resulting in poor performance and lost revenue. Automated scaling tools and predictive analytics can help optimize resource usage.
4. Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Cloud adoption enhances operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and improving productivity. Cloud platforms offer built-in automation tools to handle operational tasks such as deployment and security updates. This eliminates the need for manual maintenance and frees up internal resources for innovation and strategic initiatives.
Realizing operational and productivity gains requires proper training, change management and cloud adoption strategies. Businesses need to invest in training programs as the primary sources of expertise to help their employees quickly adapt to the cloud. This helps reduce operational overhead and improve ROI.
5. Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are critical elements that impact cloud ROI. Cloud platforms offer robust security features such as encryption, identity and access management, DDoS protection and real-time threat management.
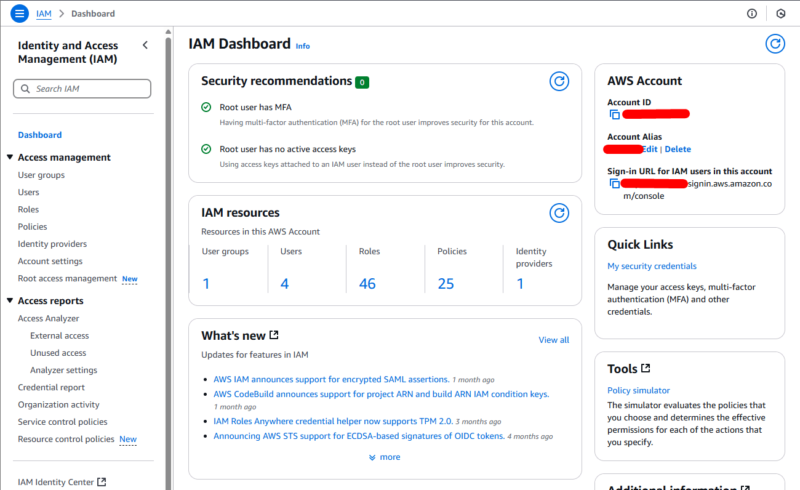
and roles to control access to AWS cloud resources.
Organizations that operate in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and finance must ensure that their cloud environments comply with relevant industry benchmarks to avoid costly fines.
Security misconfigurations pose a significant threat to cloud ROI. Failure to properly implement security features may lead to data breaches, fines and reputational damage, all of which negatively affect ROI. Regular security audits and employee training can enhance cloud security, which helps improve cloud ROI.
What Are the Advantages of Measuring Cloud ROI?
Most companies measure cloud ROI to understand the true value of their cloud investments and make informed decisions. It helps organizations optimize their strategies and justify further investments to enhance profitability and long-term sustainability.
The list below presents five key advantages of an organization measuring its cloud ROI:
- Cost optimization: Measuring ROI identifies underutilized resources and optimizes cloud spending by eliminating unused resources and adopting cost-effective pricing models.
- Informed decision-making: Understanding ROI helps businesses make data-driven decisions on scaling, resource allocation and future cloud projects.
- Operational efficiency: Organizations can use ROI analysis to highlight areas where automation and cloud-native tools can be used to enhance productivity.
- Improved business alignment: Evaluating cloud ROI ensures that cloud investments align with business objectives such as increased sales.
- Risk mitigation: Cloud ROI assessment helps detect security, compliance and performance risks early, which reduces the risk of project failure.
Methods for Increasing Cloud ROI
Businesses should prioritize increasing their cloud ROI to maximize the value of their cloud investments. Optimizing cloud ROI requires careful planning and a strategic approach to minimize expenses, improve efficiency and align cloud investments with business goals. Below are five methods that organizations can use to increase their cloud ROI.
1. Right-Sizing Resources
Many organizations overprovision resources, which leads to unnecessary costs. Right-sizing involves analyzing workload demands and adjusting resource allocation to match the actual usage. Businesses should eliminate overprovisioned resources and minimize underutilized resources, such as unattached volumes, to improve their ROI.
2. Leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
Cloud providers offer discounted pricing models, such as reserved instances and savings plans, in exchange for long-term commitments. Organizations can forecast their cloud usage and purchase resources in advance to optimize cost savings. However, this is best suited to stable, long-term workloads.
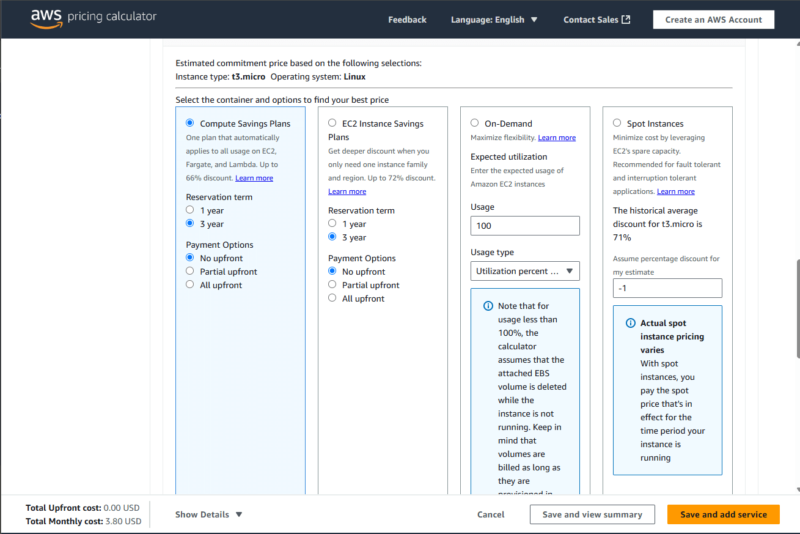
3. Automating Cloud Management and Operations
Automation reduces manual workloads, improves operational efficiency and minimizes error. Businesses should automate repetitive tasks such as deployments, backups and scaling to save time and reduce the chances of human error. Tools such as Infrastructure as Code and autoscaling can help ensure optimal resource utilization.
4. Adopting a Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Different workloads have different performance and cost requirements. Organizations can improve their ROI by placing their workloads in the most cost-effective environment.
Businesses can also leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure and Google Cloud, or use a hybrid approach to avoid vendor lock-in and take advantage of the best pricing and performance across multiple providers.
5. Continuous Cost Monitoring and Cost Governance
Cloud environments are dynamic, and costs can balloon out of control. Organizations should conduct regular audits, set up cost alerts and implement continuous monitoring tools to ensure their cloud spending aligns with their business needs. Adopting the cloud FinOps framework can help optimize expenditure and maximize the value of cloud investments.
Final Thoughts
Cloud ROI is a critical metric that helps businesses optimize their cloud investments and achieve financial and technical benefits by aligning their cloud strategies with their business goals. Calculating cloud ROI involves continuous assessment.
How do you approach cloud ROI within your organization? Please leave a comment below, share your experience or ask any questions you may have — we would love to hear your thoughts.
FAQ: Cloud ROI in Cloud Computing
ROI in cloud computing measures the benefits derived from cloud investments against the total costs incurred.
ROI in marketing cloud measures the return on investment from using cloud-based marketing tools, such as increased customer engagement and revenue growth.
Cloud migration ROI compares the long-term cost savings and benefits of moving to the cloud to the costs incurred during cloud migration.
The ROI of cloud vs on-premises infrastructure compares the cost-efficiency, scalability and flexibility of the cloud to the initial and ongoing costs of maintaining on-premises infrastructure.


